Deficiency of Carbonic Anhydrase II Results in a Urinary Concentrating Defect
- PMID: 29354070
- PMCID: PMC5760551
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2017.01108
Deficiency of Carbonic Anhydrase II Results in a Urinary Concentrating Defect
Abstract
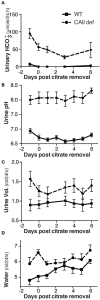
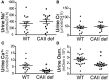
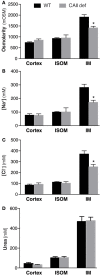
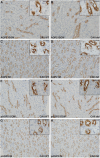
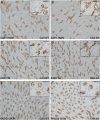
Carbonic anhydrase II (CAII) is expressed along the nephron where it interacts with a number of transport proteins augmenting their activity. Aquaporin-1 (AQP1) interacts with CAII to increase water flux through the water channel. Both CAII and aquaporin-1 are expressed in the thin descending limb (TDL); however, the physiological role of a CAII-AQP1 interaction in this nephron segment is not known. To determine if CAII was required for urinary concentration, we studied water handling in CAII-deficient mice. CAII-deficient mice demonstrate polyuria and polydipsia as well as an alkaline urine and bicarbonaturia, consistent with a type III renal tubular acidosis. Natriuresis and hypercalciuria cause polyuria, however, CAII-deficient mice did not have increased urinary sodium nor calcium excretion. Further examination revealed dilute urine in the CAII-deficient mice. Urinary concentration remained reduced in CAII-deficient mice relative to wild-type animals even after water deprivation. The renal expression and localization by light microscopy of NKCC2 and aquaporin-2 was not altered. However, CAII-deficient mice had increased renal AQP1 expression. CAII associates with and increases water flux through aquaporin-1. Water flux through aquaporin-1 in the TDL of the loop of Henle is essential to the concentration of urine, as this is required to generate a concentrated medullary interstitium. We therefore measured cortical and medullary interstitial concentration in wild-type and CAII-deficient mice. Mice lacking CAII had equivalent cortical interstitial osmolarity to wild-type mice: however, they had reduced medullary interstitial osmolarity. We propose therefore that reduced water flux through aquaporin-1 in the TDL in the absence of CAII prevents the generation of a maximally concentrated medullary interstitium. This, in turn, limits urinary concentration in CAII deficient mice.
Keywords: aquaporin-1; carbonic anhydrase II; metabolic; polyuria; urine concentration.
Figures



References
-
- Beggs M. R., Appel I., Svenningsen P., Skjødt K., Alexander R. T., Dimke H. (2017). Expression of transcellular and paracellular calcium and magnesium transport proteins in renal and intestinal epithelia during lactation. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 313, F629–F640. 10.1152/ajprenal.00680.2016 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

