Towards Integrating Distributed Energy Resources and Storage Devices in Smart Grid
- PMID: 29354654
- PMCID: PMC5774658
- DOI: 10.1109/JIOT.2016.2640563
Towards Integrating Distributed Energy Resources and Storage Devices in Smart Grid
Abstract
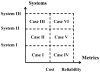
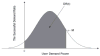
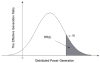
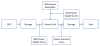
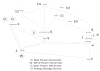
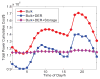
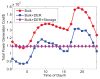
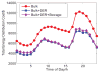
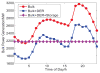
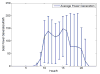
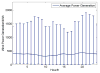
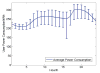
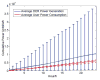
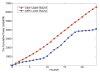
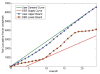
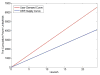
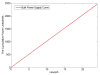
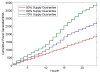
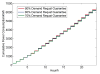
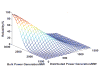
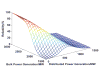
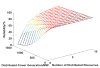
Internet of Things (IoT) provides a generic infrastructure for different applications to integrate information communication techniques with physical components to achieve automatic data collection, transmission, exchange, and computation. The smart grid, as one of typical applications supported by IoT, denoted as a re-engineering and a modernization of the traditional power grid, aims to provide reliable, secure, and efficient energy transmission and distribution to consumers. How to effectively integrate distributed (renewable) energy resources and storage devices to satisfy the energy service requirements of users, while minimizing the power generation and transmission cost, remains a highly pressing challenge in the smart grid. To address this challenge and assess the effectiveness of integrating distributed energy resources and storage devices, in this paper we develop a theoretical framework to model and analyze three types of power grid systems: the power grid with only bulk energy generators, the power grid with distributed energy resources, and the power grid with both distributed energy resources and storage devices. Based on the metrics of the power cumulative cost and the service reliability to users, we formally model and analyze the impact of integrating distributed energy resources and storage devices in the power grid. We also use the concept of network calculus, which has been traditionally used for carrying out traffic engineering in computer networks, to derive the bounds of both power supply and user demand to achieve a high service reliability to users. Through an extensive performance evaluation, our data shows that integrating distributed energy resources conjointly with energy storage devices can reduce generation costs, smooth the curve of bulk power generation over time, reduce bulk power generation and power distribution losses, and provide a sustainable service reliability to users in the power grid.
Keywords: Smart grid; distributed energy resources; energy storage; performance evaluation.
Figures




References
-
- Xu G, Moulema P, Yu W. Integrating distributed energy resources in smart grid: Modeling and analysis. Proceedings of IEEE Energy Tech. 2013
-
- Stankovic JA. Research directions for the internet of things. Internet of Things Journal, IEEE. 2014;1(1):3–9.
-
- Pan J, Jain R, Paul S, Vu T, Saifullah A, Sha M. An internet of things framework for smart energy in buildings: Designs, prototype, and experiments. Internet of Things Journal, IEEE. 2015;2(6):527–537.
-
- Wang Y, Mao S, Nelms R. Distributed online algorithm for optimal real-time energy distribution in the smart grid. Internet of Things Journal, IEEE. 2014;1(1):70–80.
-
- Bao H, Lu R. A new differentially private data aggregation with fault tolerance for smart grid communications. Internet of Things Journal, IEEE. 2015;2(3):248–258.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
