Multiplex polymerase chain reaction of genetic markers for detection of potentially pathogenic environmental Legionella pneumophila isolates
- PMID: 29355148
- PMCID: PMC5793476
- DOI: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_623_16
Multiplex polymerase chain reaction of genetic markers for detection of potentially pathogenic environmental Legionella pneumophila isolates
Abstract
Background & objectives: Genomic constitution of the bacterium Legionella pneumophila plays an important role in providing them a pathogenic potential. Here, we report the standardization and application of multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for the detection of molecular markers of pathogenic potential in L. pneumophila in hospital environment.
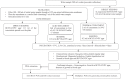
Methods: Culture of the standard strains of L. pneumophila was performed in buffered charcoal-yeast extract agar with L-cysteine at p H 6.9. Primers were designed for multiplex PCR, and standardization for the detection of five markers annotated to L. pneumophila plasmid pLPP (11A2), lipopolysaccharide synthesis (19H4), CMP-N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase (10B12), conjugative coupling factor (24B1) and hypothetical protein (8D6) was done. A total of 195 water samples and 200 swabs were collected from the hospital environment. The bacterium was isolated from the hospital environment by culture and confirmed by 16S rRNA gene PCR and restriction enzyme analysis. A total of 45 L. pneumophila isolates were studied using the standardized multiplex PCR.
Results: The PCR was sensitive to detect 0.1 ng/μl DNA and specific for the two standard strains used in the study. Of the 45 hospital isolates tested, 11 isolates had four markers, 12 isolates had three markers, 10 isolates had two markers, nine isolates had one marker and three isolates had none of the markers. None of the isolates had all the five markers.
Interpretation & conclusions: The findings of this study showed the presence of gene markers of pathogenic potential of the bacterium L. pneumophila. However, the genomic constitution of the environmental isolates should be correlated with clinical isolates to prove their pathogenic potential. Rapid diagnostic methods such as multiplex PCR reported here, for elucidating gene markers, could help in future epidemiological studies of bacterium L. pneumophila.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
PCR methods for the rapid detection and identification of four pathogenic Legionella spp. and two Legionella pneumophila subspecies based on the gene amplification of gyrB.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011 Aug;91(3):777-87. doi: 10.1007/s00253-011-3283-6. Epub 2011 May 29. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21626022
-
Detection and identification of Legionella pneumophila by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of the RNA polymerase gene (rpoB).J Microbiol Methods. 2003 Sep;54(3):325-37. doi: 10.1016/s0167-7012(03)00065-4. J Microbiol Methods. 2003. PMID: 12842479
-
Design and implementation of a protocol for the detection of Legionella in clinical and environmental samples.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2008 Oct;62(2):125-32. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2008.05.004. Epub 2008 Jul 14. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2008. PMID: 18621500
-
Detection and quantification of Legionella pneumophila DNA in serum: case reports and review of the literature.J Med Microbiol. 2006 May;55(Pt 5):639-642. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.46453-0. J Med Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16585654 Review.
-
[Legionella, Legionnaires' disease].Med Sci (Paris). 2012 Jun-Jul;28(6-7):639-45. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2012286018. Epub 2012 Jul 16. Med Sci (Paris). 2012. PMID: 22805141 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Distribution of Virulence Genes and Sequence-Based Types Among Legionella pneumophila Isolated From the Water Systems of a Tertiary Care Hospital in India.Front Public Health. 2020 Nov 23;8:596463. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.596463. eCollection 2020. Front Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33330340 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yu VL, Plouffe JF, Pastoris MC, Stout JE, Schousboe M, Widmer A, et al. Distribution of Legionella species and serogroups isolated by culture in patients with sporadic community-acquired legionellosis: An international collaborative survey. J Infect Dis. 2002;186:127–8. - PubMed
-
- Cunha BA, Burillo A, Bouza E. Legionnaires’ disease. Lancet. 2016;387:376–85. - PubMed
-
- Harrison TG, Doshi N, Fry NK, Joseph CA. Comparison of clinical and environmental isolates of Legionella pneumophila obtained in the UK over 19 years. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2007;13:78–85. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
