E-learning for health professionals
- PMID: 29355907
- PMCID: PMC6491176
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011736.pub2
E-learning for health professionals
Abstract
Background: The use of e-learning, defined as any educational intervention mediated electronically via the Internet, has steadily increased among health professionals worldwide. Several studies have attempted to measure the effects of e-learning in medical practice, which has often been associated with large positive effects when compared to no intervention and with small positive effects when compared with traditional learning (without access to e-learning). However, results are not conclusive.
Objectives: To assess the effects of e-learning programmes versus traditional learning in licensed health professionals for improving patient outcomes or health professionals' behaviours, skills and knowledge.
Search methods: We searched CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase, five other databases and three trial registers up to July 2016, without any restrictions based on language or status of publication. We examined the reference lists of the included studies and other relevant reviews. If necessary, we contacted the study authors to collect additional information on studies.
Selection criteria: Randomised trials assessing the effectiveness of e-learning versus traditional learning for health professionals. We excluded non-randomised trials and trials involving undergraduate health professionals.
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently selected studies, extracted data and assessed risk of bias. We graded the certainty of evidence for each outcome using the GRADE approach and standardised the outcome effects using relative risks (risk ratio (RR) or odds ratio (OR)) or standardised mean difference (SMD) when possible.
Main results: We included 16 randomised trials involving 5679 licensed health professionals (4759 mixed health professionals, 587 nurses, 300 doctors and 33 childcare health consultants).When compared with traditional learning at 12-month follow-up, low-certainty evidence suggests that e-learning may make little or no difference for the following patient outcomes: the proportion of patients with low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol of less than 100 mg/dL (adjusted difference 4.0%, 95% confidence interval (CI) -0.3 to 7.9, N = 6399 patients, 1 study) and the proportion with glycated haemoglobin level of less than 8% (adjusted difference 4.6%, 95% CI -1.5 to 9.8, 3114 patients, 1 study). At 3- to 12-month follow-up, low-certainty evidence indicates that e-learning may make little or no difference on the following behaviours in health professionals: screening for dyslipidaemia (OR 0.90, 95% CI 0.77 to 1.06, 6027 patients, 2 studies) and treatment for dyslipidaemia (OR 1.15, 95% CI 0.89 to 1.48, 5491 patients, 2 studies). It is uncertain whether e-learning improves or reduces health professionals' skills (2912 health professionals; 6 studies; very low-certainty evidence), and it may make little or no difference in health professionals' knowledge (3236 participants; 11 studies; low-certainty evidence).Due to the paucity of studies and data, we were unable to explore differences in effects across different subgroups. Owing to poor reporting, we were unable to collect sufficient information to complete a meaningful 'Risk of bias' assessment for most of the quality criteria. We evaluated the risk of bias as unclear for most studies, but we classified the largest trial as being at low risk of bias. Missing data represented a potential source of bias in several studies.
Authors' conclusions: When compared to traditional learning, e-learning may make little or no difference in patient outcomes or health professionals' behaviours, skills or knowledge. Even if e-learning could be more successful than traditional learning in particular medical education settings, general claims of it as inherently more effective than traditional learning may be misleading.
Conflict of interest statement
AV: none known.
RB: none known.
KK: none known.
GR: none known.
DC: none known.
VP: none known.
IT: none known.
LM: none known.
Figures
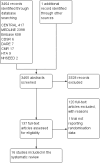


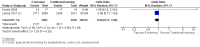
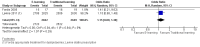
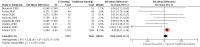
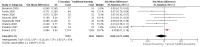



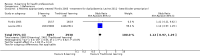




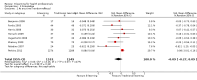
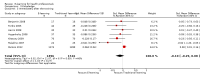

Comment in
-
E-learning may be no better than traditional teaching for continuing education of health professionals.Evid Based Nurs. 2019 Apr;22(2):52. doi: 10.1136/ebnurs-2018-102927. Epub 2018 Dec 1. Evid Based Nurs. 2019. PMID: 30504452 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Benjamin 2008 {published data only}
-
- Benjamin SE, Tate DF, Bangdiwala SI, Neelon BH, Ammerman AS, Dodds JM, et al. Preparing child care health consultants to address childhood overweight: a randomised controlled trial comparing web to in‐person training. Maternal Child Health Journal 2008;12(5):662‐9. - PubMed
Bredesen 2016 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bredesen IM, Bjøro K, Gunningberg L, Hofoss D. Effect of e‐learning program on risk assessment and pressure ulcer classification ‐ a randomized study. Nurse Education Today 2016;40:191‐7. - PubMed
Fordis 2005 {published data only}
-
- Fordis M, King JE, Ballantyne CM, Jones PH, Schneider KH, Spann SJ, et al. Comparison of the instructional efficacy of Internet‐based CME with live interactive CME workshops: a randomised controlled trial. JAMA 2005;294(9):1043‐51. - PubMed
Harris 2008 {published data only}
-
- Harris JM Jr, Elliott TE, Davis BE, Chabal C, Fulginiti JV, Fine PG. Educating generalist physicians about chronic pain: live experts and online education can provide durable benefits. Pain Medicine 2008;9(5):555‐63. - PubMed
Horiuchi 2009 {published data only}
-
- Horiuchi S, Yaju Y, Koyo M, Sakyo Y, Nakayama K. Evaluation of a web‐based graduate continuing nursing education program in Japan: a randomised controlled trial. Nurse Education Today 2009;29(2):140‐9. - PubMed
Hugenholtz 2008 {published data only}
Khatony 2009 {published data only}
Le 2010 {published data only}
-
- Le TT, Rait MA, Jarlsberg LG, Eid NS, Cabana MD. A randomised controlled trial to evaluate the effectiveness of a distance asthma learning program for paediatricians. Journal of Asthma 2010;47(3):245‐50. - PubMed
Levine 2011 {published data only}
-
- Levine DA, Funkhouser EM, Houston TK, Gerald JK, Johnson‐Roe N, Allison JJ, et al. Improving care after myocardial infarction using a 2‐year Internet‐delivered intervention: the Department of Veterans Affairs myocardial infarction‐plus cluster‐randomised trial. Archives of Internal Medicine 2011;171(21):1910‐7. - PMC - PubMed
Mäkinen 2006 {published data only}
-
- Mäkinen M, Castrèn M, Tolska T, Nurmi J, Niemi‐Murola L. Teaching basic life support to nurses. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2006;23(4):327‐31. - PubMed
Maloney 2011 {published data only}
Paladino 2007 {published data only}
-
- Padalino Y, Peres HH. E‐learning: a comparative study for knowledge apprehension among nurses. Revista Latino‐Americana De Enfermagem 2007;15(3):397‐403. - PubMed
Perkins 2012 {published data only}
-
- Perkins GD, Kimani PK, Bullock I, Clutton‐Brock T, Davies RP, Gale M, et al. Improving the efficiency of advanced life support training: a randomised, controlled trial. Annals of Internal Medicine 2012;3(157):19‐28. - PubMed
Sheen 2008 {published data only}
-
- Sheen ST, Chang WY, Chen HL, Chao HL, Tseng CP. E‐Learning education program for registered nurses: the experience of a teaching medical centre. Journal of Nursing Research 2008;16(3):195‐201. - PubMed
Simonsen 2014 {published data only}
Wilson‐Sands 2015 {published data only}
-
- Wilson‐Sands C, Brahn P, Graves K. The effect of instructional method on cardiopulmonary resuscitation skill performance. Journal for Nurses in Professional Development 2015;31(5):E1‐7. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Alfieri 2012 {published data only}
-
- Alfieri J, Portelance L, Souhami L, Steinert Y, McLeod P, Gallant F, et al. Development and impact evaluation of an e‐learning radiation oncology module. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics 2012;82(3):e573‐80. - PubMed
Allison 2005 {published data only}
-
- Allison JJ, Kiefe CI, Wall T, Casebeer L, Ray MN, Spettell CM, et al. Multicomponent Internet continuing medical education to promote chlamydia screening. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 2005;28(3):285‐90. - PubMed
Anderson 2006 {published data only}
-
- Anderson C. Training efforts to reduce reports of workplace violence in a community health care facility. Journal of Professional Nursing 2006;22(5):289‐95. - PubMed
Andolsek 2013 {published data only}
-
- Andolsek K, Rosenberg MT, Abdolrasulnia M, Stowell SA, Gardner AJ. Complex cases in primary care: report of a CME‐certified series addressing patients with multiple co‐morbidities. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2013;67(9):911‐7. - PubMed
Bayar 2009 {published data only}
-
- Bayar MR, Poyraz BC, Aksoy‐Poyraz C, Arikan MK. Reducing mental illness stigma in mental health professionals using a web‐based approach. Israeli Journal of Psychiatry Related Sciences 2009;46(3):226‐30. - PubMed
Beckley 2000 {published data only}
-
- Beckley S, Stenhouse E, Greene K. The development and evaluation of a computer‐assisted teaching programme for intrapartum fetal monitoring. BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology 2000;107(9):1138‐44. - PubMed
Beeckman 2008 {published data only}
-
- Beeckman D, Schoonhoven L, Boucqué H, Maele G, Defloor T. Pressure ulcers: e‐learning to improve classification by nurses and nursing students. Journal of Clinical Nursing 2008;17(13):1697‐707. - PubMed
Bello 2005 {published data only}
-
- Bello G, Pennisi MA, Maviglia R, Maggiore SM, Bocci MG, Montini L, et al. Online vs live methods for teaching difficult airway management to anesthesiology residents. Intensive Care Medicine 2005;31(4):547‐52. - PubMed
Benedict 2013 {published data only}
Beyea 2008 {published data only}
-
- Beyea JA, Wong E, Bromwich M, Weston WW, Fung K. Evaluation of a particle repositioning maneuver Web‐based teaching module. Laryngoscope 2008;118(1):175‐80. - PubMed
Bode 2012 {published data only}
-
- Bode R, Barcellona DS, Scharlatt K, Bulloch B, Caputo G. E‐learning software to enhance paediatric medical education. Academic Pediatrics 2012;12(3):e13.
Boespflug 2015 {published data only}
-
- Boespflug AG, Dalle S, Thomas L. Enhancement of customary dermoscopy education with spaced education e‐learning: a prospective controlled trial. JAMA Dermatology 2015;151(8):847‐53. - PubMed
Bonevski 1999 {published data only}
-
- Bonevski B, Sanson‐Fisher RW, Campbell E, Carruthers A, Reid AL, Ireland M. Randomized controlled trial of a computer strategy to increase general practitioner preventive care. Preventive Medicine 1999;29(6):478‐86. - PubMed
Browne 2004 {published data only}
-
- Browne L, Mehra S, Rattan R, Thomas G. Comparing lecture and e‐learning as pedagogies for new and experienced professionals in dentistry. British Dental Journal 2004;197:95‐97. - PubMed
Buijze 2012 {published data only}
Butler 2012 {published data only}
Butzlaff 2004 {published data only}
-
- Butzlaff M, Vollmar HC, Floer B, Koneczny N, Isfort J, Lange S. Learning with computerized guidelines in general practice? A randomised controlled trial. Family Practice 2004;21(2):183‐8. - PubMed
Carney 2011 {published data only}
Carney 2012 {published data only}
Casap 2011 {published data only}
-
- Casap N, Nadel S, Tarazi E, Weiss EI. Evaluation of a navigation system for dental implantation as a tool to train novice dental practitioners. Journal of Oral Maxillofacial Surgery 2011;69(19):2548‐56. - PubMed
Chan 1999 {published data only}
-
- Chan DH, Leclair K, Kaczorowski J. Problem‐based small‐group learning via the Internet among community family physicians: a randomised controlled trial. M.D. Computing: Computers in Medical Practice 1999;16(3):54‐8. - PubMed
Chenkin 2008 {published data only}
-
- Chenkin J, Lee S, Huynh T, Bandiera G. Procedures can be learned on the Web: a randomised study of ultrasound‐guided vascular access training. Academic Emergency Medicine 2008;15(10):949‐54. - PubMed
Chung 2004 {published data only}
-
- Chung S, Mandl KD, Shannon M, Fleisher GR. Efficacy of an educational Web site for educating physicians about bio‐terrorism. Academic Emergency Medicine 2004;11(2):143‐8. - PubMed
Cook 2008 {published data only}
Crenshaw 2010 {published data only}
Curtis 2007 {published data only}
-
- Curtis JR, Westfall AO, Allison J, Becker A, Melton ME, Freeman A, et al. Challenges in improving the quality of osteoporosis care for long‐term glucocorticoid users: a prospective randomised trial. Archives of Internal Medicine 2007;167(6):591‐6. - PubMed
De Beurs 2015 {published data only}
-
- Beurs DP, Groot MH, Keijser J, Mokkenstorm J, Duijn E, Winter RF, et al. The effect of an e‐learning supported Train‐the‐Trainer programme on implementation of suicide guidelines in mental health care. Journal of Affective Disorders 2015;175:446‐53. - PubMed
De Beurs 2016 {published data only}
-
- Beurs DPdG, Keijser J. van Duijn E, Winter RF, Kerkhof AJ. Evaluation of benefit to patients of training mental health professionals in suicide guidelines: cluster randomised trial. British Journal of Psychiatry 2016;208(5):477‐83. - PubMed
Dimeff 2011 {published data only}
-
- Dimeff LA, Woodcock EA, Harned MS, Beadnell B. Can dialectical behavior therapy be learned in highly structured learning environments? Results from a randomised controlled dissemination trial. Behavioral Therapy 2011;42(2):263‐75. - PubMed
Esche 2015 {published data only}
-
- Esche CA, Warren JI, Woods AB, Jesada EC, Iliuta R. Traditional classroom education versus computer‐based learning: how nurses learn about pressure ulcers. Journal of Nurses Professional Development 2015;31(1):21‐7. - PubMed
Estrada 2010 {published data only}
-
- Estrada C, Salanitro A, Safford M, Curry W, Williams J, Ovalle F, Payne‐Foster P, et al. A cluster‐randomized trial of a web‐based physician intervention to improve diabetes care. American Federation for Medical Research Southern Regional Meeting; 2010 February 25‐27; New Orleans, LA. Journal of Investigative Medicine: available from www.academicpeds.org/regions/pdfs/ProgramSRM2010.pdf, 2010. [Abstract 512]
Estrada 2011 {published data only}
Fary 2015 {published data only}
-
- Fary RES, Chua J, Ranelli S, Chan M, Briggs AM. Policy‐into‐practice for rheumatoid arthritis: randomized controlled trial and cohort study of e‐learning targeting improved physiotherapy management. Arthritis Care and Research 2015;67(7):913‐22. - PubMed
Fisher 2014 {published data only}
-
- Fisher WW, Luczynski KC, Hood SA, Lesser DA, Machado MA, Piazza CC. Preliminary findings of a randomised clinical trial of a virtual training program for applied behavior analysis technicians. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders 2014;8(9):1044–54.
Foroudi 2013 {published data only}
-
- Foroudi F, Pham D, Bressel M, Tongs D, Rolfo A, Styles C, et al. The utility of e‐Learning to support training for a multicentre bladder online adaptive radiotherapy trial (TROG 10.01‐BOLART). Radiotherapy and Oncology 2013;109(1):165‐9. - PubMed
Fox 2001 {published data only}
-
- Fox N, O'Rourke A, Roberts C, Walker J. Change management in primary care: design and evaluation of an Internet‐delivered course. Medical Education 2001;35(8):803‐5. - PubMed
Franchi 2016 {published data only}
Funk 2010 {published data only}
Gerbert 2002 {published data only}
-
- Gerbert B, Bronstone A, Maurer T, Berger T, McPhee SJ, Caspers N. The effectiveness of an Internet‐based tutorial in improving primary care physicians' skin cancer triage skills. Journal of Cancer Education 2002;17(1):7‐11. - PubMed
Ghoncheh 2014 {published data only}
Gordon 2011a {published data only}
-
- Gordon M1, Chandratilake M, Baker P. Improved junior paediatric prescribing skills after a short e‐learning intervention: a randomised controlled trial. Archives of Disease in Childhood 2011;96(12):1191‐1194. - PubMed
Gordon 2011b {published data only}
-
- Gordon MA, Baker P, Chandratilake M. Is a short e‐learning course effective at improving paediatric prescribing skills among foundation doctors? An open label randomised controlled trial. Archives of Disease in Childhood 2011;96:A22‐A23. - PubMed
Gordon 2013a {published data only}
Gordon 2013b {published data only}
-
- Gordon M, Chandratilake M, Baker P. Low fidelity, high quality: a model for e‐learning. Clinical Teacher 2013;10:258‐63. - PubMed
Granpeesheh 2010 {published data only}
-
- Granpeesheh D, Tarbox J, Dixon RD, Peters CA, Thompson K, Kenzer A. Evaluation of an eLearning tool for training behavioral therapists in academic knowledge of applied behavior analysis. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders 2010;4(1):11‐7.
Gyorki 2013 {published data only}
-
- Gyorki DE, Shaw T, Nicholson J, Baker C, Pitcher M, Skandarajah A, et al. Improving the impact of didactic resident training with online spaced education. ANZ Journal of Surgery 2013;83(6):477‐80. - PubMed
Hansen 2007 {published data only}
-
- Hansen KE, Rosenblatt ER, Gjerde CL, Crowe ME. Can an online osteoporosis lecture increase physician knowledge and improve patient care?. Journal of Clinical Densitometry: the Official Journal of the International Society for Clinical Densitometry 2007;10(1):10‐20. - PubMed
Harris 2013 {published data only}
Hearty 2013 {published data only}
-
- Hearty T, Maizels M, Pring M, Mazur J, Liu R, Sarwark J, et al. Orthopaedic resident preparedness for closed reduction and pinning of paediatric supracondylar fractures is improved by e‐learning: a multisite randomised controlled study. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume 2013;4(95):e1261‐7. - PubMed
Houwink 2014 {published data only}
Jensen 2009 {published data only}
-
- Jensen ML, Mondrup F, Lippert F, Ringsted C. Using e‐learning for maintenance of ALS competence. Resuscitation 2009;80(8):903‐8. - PubMed
Kemper 2002 {published data only}
-
- Kemper KJ, Amata‐Kynvi A, Sanghavi D, Whelan JS, Dvorkin L, Woolf A, et al. Randomized trial of an Internet curriculum on herbs and other dietary supplements for health care professionals. Academic Medicine 2002;77(9):882‐9. - PubMed
Kerfoot 2010 {published data only}
-
- Kerfoot BP. Adaptive spaced education improves learning efficiency: a randomised controlled trial. Journal of Urology 2010;183(2):678‐81. - PubMed
Kerfoot 2012 {published data only}
-
- Kerfoot BP, Baker H. An online spaced‐education game for global continuing medical education: a randomised trial. Annals of Surgery 2012;256(1):33‐8. - PubMed
Khanal 2014 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Khanal P, Vankipuram A, Ashby A, Vankipuram M, Gupta A, Drumm‐Gurnee D, et al. Collaborative virtual reality based advanced cardiac life support training simulator using virtual reality principles. Journal of Biomedical Informatics 2014;51:49‐59. - PubMed
Kim 2014 {published data only}
-
- Kim JH, Shin JS. Effects of an online problem‐based learning program on sexual health care competencies among oncology nurses: a pilot study. Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing 2014;45(9):393‐401. - PubMed
Kobak 2005 {published data only}
-
- Kobak KA, Engelhardt N, Lipsitz JD. Enriched rater training using Internet based technologies: a comparison to traditional rater training in a multi‐site depression trial. Journal of Psychiatric Research 2006;40(3):192‐9. - PubMed
Kontio 2011 {published data only}
-
- Kontio R, Lahti M, Pitkänen A, Joffe G, Putkonen H, Hätönen H, et al. Impact of eLearning course on nurses' professional competence in seclusion and restraint practices: a randomised controlled study. Journal of Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing 2011;18(9):813‐21. - PubMed
Kontio 2013 {published data only}
-
- Kontio R, Hätönen H, Joffe G, Pitkänen A, Lahti M, Välimäki M. Impact of eLearning course on nurses' professional competence in seclusion and restraint practices: 9‐month follow‐up results of a randomised controlled study. Journal of Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing 2013;20(5):411‐8. - PubMed
Kontio 2014 {published data only}
-
- Kontio R, Pitkänen A, Joffe G, Katajisto J, Välimäki M. eLearning course may shorten the duration of mechanical restraint among psychiatric inpatients: a cluster‐randomized trial. Nordic Journal of Psychiatry 2014;68(7):443‐9. - PubMed
Legris 2011 {published data only}
-
- Legris MÈ, Séguin NC, Desforges K, Sauvé P, Lord A, Bell R, et al. Pharmacist Web‐based training program on medication use in chronic kidney disease patients: impact on knowledge, skills, and satisfaction. Journal of Continuing Education in the Health Professions 2011;31(3):140‐50. - PubMed
Liaw 2015 {published data only}
Little 2013 {published data only}
Liu 2014a {published data only}
-
- Liu WI, Rong JR, Liu CY. Using evidence‐integrated e‐learning to enhance case management continuing education for psychiatric nurses: A randomised controlled trial with follow‐up. Nurse Education Today 2014;34:1361‐7. - PubMed
Liu 2014b {published data only}
-
- Liu WI, Chu RC, Chen SC. The development and preliminary effectiveness of a nursing case management e‐learning program. Computers, Informatics, Nursing 2014;32(7):343‐52. - PubMed
Lu 2009 {published data only}
-
- Lu DF, Lin ZC, Li YJ. Effects of a Web‐based course on nursing skills and knowledge learning. Journal of Nursing Education 2009;48(2):70‐7. - PubMed
Maloney 2012 {published data only}
Markova 2013 {published data only}
-
- Markova A, Weinstock MA, Risica P, Kirtania U, Shaikh W, Ombao H, et al. Effect of a web‐based curriculum on primary care practice: basic skin cancer triage trial. Family Medicine 2013;45(8):558‐68. - PubMed
Marshall 2014 {published data only}
-
- Marshall E, York J, Magruder K, Yeager D, Knapp R, Santis ML, et al. Implementation of online suicide‐specific training for VA providers. Academic Psychiatry 2014;38(5):66‐74. - PubMed
McCormack 2012 {published data only}
-
- Cormack H, Bipasha C. Using a web‐based electronic resource to study cardiac anatomy. Clinical Anatomy 2012;25(6):798‐812.
McCrow 2014 {published data only}
-
- McCrow JS, Beattie ER. Delirium knowledge and recognition: a randomized controlled trial of a web‐based educational intervention for acute care nurses. Nurse Education Today 2014;34(6):912‐7. - PubMed
Meckfessel 2011 {published data only}
-
- Meckfessel S, Stühmer C, Bormann KH, Kupka T, Behrends M, Matthies H, et al. Introduction of e‐learning in dental radiology reveals significantly improved results in final examination. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2011;39(1):40‐8. - PubMed
Midmer 2006 {published data only}
-
- Midmer D, Kahan M, Marlow B. Effects of a distance learning program on physicians' opioid‐ and benzodiazepine‐prescribing skills. Journal of Continuing Education in the Health Professions 2006;26(4):294‐301. - PubMed
Moja 2008 {published data only}
-
- Moja L, Moschetti I, Cinquini M, Sala V, Compagnoni A, Duca P, et al. Clinical evidence continuous medical education: a randomised educational trial of an open access e‐learning program for transferring evidence‐based information ‐ ICEKUBE (Italian Clinical Evidence Knowledge Utilization Behaviour Evaluation) ‐ study protocol. Implementation Science 2008;3(37):1‐11. - PMC - PubMed
Moorthy 2003 {published data only}
-
- Moorthy K, Jiwanji M, Shah J, Bello F, Munoz Y, Darzi A. Validation of a web‐based training tool for lumbar puncture. Medicine Meets Virtual Reality 2003;94:219‐25. - PubMed
Moreira 2015 {published data only}
NCT00394017 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT00394017. The use of reminders in implementing an e‐learning program in general practice [Implementation of an E‐learning Program in Diagnostic Evaluation of Dementia by Reminders: A RCT Among General Practitioners in Copenhagen]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00394017?term=NCT00394017&rank=1 First received October 26, 2006.
NCT00815724 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT00815724. Evaluating a distance learning asthma education program for paediatricians (The DALI Study) [Distributed Asthma Learning Initiative]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00815724?term=NCT00815724&rank=1 First received December 29, 2008.
NCT00934141 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT00934141. Evaluating improvement strategies in addiction treatment (NIATx 200) [Randomized Control Trial (RCT) Evaluating Improvement Strategies in Addiction Treatment]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00934141?term=NCT00934141&rank=1 First received July 6, 2009.
NCT00962455 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT00962455. Feedback reports and e‐learning in primary care spirometry (FRESCO) [Feedback Reports and E‐learning to Support Spirometry Test Performance in Dutch Family Practices]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00962455?term=NCT00962455&rank=1 First received August 17, 2009.
NCT01326936 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT01326936. Online primary care physician (PCP) training in screening, brief Intervention, referral, and treatment [Fast Track SBIR Study Online PCP Training in Screening, Brief Intervention, Referral, and Treatment]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01326936?term=NCT01326936&rank=1 First received March 29, 2011.
NCT01427660 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT01427660. iDecide.Decido: diabetes medication decision support study [Technologically Enhanced Community Health Worker (CHW) Delivery of Personalized Diabetes Information]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01427660?term=NCT01427660&rank=1 First received August 31, 2014.
NCT01834521 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT01834521. Web‐based screening and tailored support (ENCOURAGE) [Web‐based Screening and Tailored Support for Breast Cancer Patients at the Onset of the Survivorship Phase]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01834521?term=NCT01834521&rank=1 First received April 9, 2013.
NCT01955005 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT01955005. Use of the My HealtheVet for Health Information Sharing [Pilot of My HealtheVet Training to Improve Co‐Managed Care for Veterans]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01955005?term=NCT01955005&rank=1 First received August 20, 2013.
Nesterowicz 2015 {published data only}
-
- Nesterowicz K, Fereshtehnejad SM, Edelbring S. e‐learning in continuing pharmacy education is effective and just as accepted as on‐site learning. Pharmacy Education 2015;15(1):22‐26.
Paul 2013 {published data only}
-
- Paul CL, Piterman L, Shaw J, Kirby C, Sanson‐Fisher RW, Carey ML, et al. Diabetes in rural towns: effectiveness of continuing education and feedback for healthcare providers in altering diabetes outcomes at a population level: protocol for a cluster randomised controlled trial. Implementation Science 2013;13(8):30. - PMC - PubMed
Pearce‐Smith 2005 {published data only}
-
- Pearce‐Smith N. Issues and problems for librarians conducting research ‐ an example of a randomised controlled trial comparing the effect of e‐learning with a taught workshop on the knowledge and search skills of health professionals. Third International Evidence‐Based Librarianship Conference. Brisbane, Australia, 2005 Oct 16‐19, Brisbane, Australia.
Pelayo‐Alvarez 2011 {published data only}
Perkins 2010 {published data only}
-
- Perkins GD, Kimani PK, Bullock I, Clutton‐Brock T, Davies RP, Gale M, et al. Electronic Advanced Life Support Collaborators. Improving the efficiency of advanced life support training: a randomised, controlled trial. Annals of Internal Medicine 2012;157(1):19‐28. - PubMed
Pham 2013 {published data only}
-
- Pham T, Hacquard‐Bouder C, Roux F, Cotten A, Loeuille D, Malghem J, et al. SAT0417 Impact of an online training on MRI sacroiliac joints reading and active SPA sacroiliitis diagnosing. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2013;71:613.
Pham 2016 {published data only}
-
- Pham DH, Foroudi F, Kron T, Bressel M, Hilder B, Chesson B. A multidisciplinary evaluation of a web‐based eLearning training programme for SAFRON II (TROG 13.01): a multicentre randomised study of stereotactic radiotherapy for lung metastases. Clinical Oncology (Royal College of Radiologists) 2016;28(9):e101‐8. - PubMed
Platz 2010 {published data only}
-
- Platz E, Goldflam K, Mennicke M, Parisini E, Christ M, Hohenstein C. Comparison of web‐versus classroom‐based basic ultrasonographic and EFAST training in 2 European hospitals. Annals of Emergency Medicine 2010;56(6):660‐7. - PubMed
Rafalski 2004 {published data only}
-
- Rafalski V, Andreeva I. Promoting access to Cochrane Collaboration outputs in developing countries: the possible role of post‐graduate distance education. 12th Cochrane Colloquium: Bridging the Gaps; 2004 October 2‐6; Ottawa (ON). 2004:177 p.
Rankin 2013 {published data only}
-
- Rankin JA, Then KL, Atack L. Can emergency nurses' triage skills be improved by online learning? Results of an experiment. Journal of Emergency Nursing 2013;39(1):20‐6. - PubMed
Ruzek 2012 {published data only}
Schermer 2011 {published data only}
Schopf 2012 {published data only}
Sharma 2013 {published data only}
-
- Sharma V, Chamos C, Valencia O, Meineri M, Fletcher SN. The impact of Internet and simulation‐based training on transoesophageal echocardiography learning in anaesthetic trainees: a prospective randomised study. Anaesthesia 2013;68(6):621‐7. - PubMed
Shaw 2011 {published data only}
-
- Shaw T, Long A, Chopra S, Kerfoot BP. Impact on clinical behavior of face‐to‐face continuing medical education blended with online spaced education: a randomised controlled trial. Journal of Continuing Education in the Health Professions 2011;31(2):103‐8. - PubMed
Simpson 2009 {published data only}
-
- Simpson SA, Butler CC, Hood K, Cohen D, Dunstan F, Evans MR, et al. Stemming the Tide of Antibiotic Resistance (STAR): a protocol for a trial of a complex intervention addressing the 'why' and 'how' of appropriate antibiotic prescribing in general practice. BMC Family Practice 2009;10(20):1‐10. - PMC - PubMed
Smeekens 2011 {published data only}
-
- Smeekens AE, Broekhuijsen‐van Henten DM, Sittig JS, Russel IM, Cate OT, Turner NM, et al. Successful e‐learning programme on the detection of child abuse in emergency departments: a randomised controlled trial. Archives of Disease in Childhood 2011;96(4):330‐4. - PubMed
Soh 2010 {unpublished data only}
-
- Soh BP, Reed W, Poulos A, Brennan PC. Visual search strategy of naive readers interpreting mammograms before and after an e‐learning tutorial. Proceedings of Singapore Healthcare 2010;19:S214.
Stein 2015 {published data only}
Stewart 2005 {published data only}
-
- Stewart M, Marshall JN, Østbye T, Feightner JW, Brown JB, Harris S, et al. Effectiveness of case‐based on‐line learning of evidence‐based practice guidelines. Family Medicine 2005;37(2):131‐8. - PubMed
Sung 2008 {published data only}
-
- Sung YH, Kwon IG, Ryu E. Blended learning on medication administration for new nurses: integration of e‐learning and face‐to‐face instruction in the classroom. Nurse Education Today 2008;28(8):943‐52. - PubMed
Thompson 2012 {published data only}
Tung 2014 {published data only}
Valish 1975 {published data only}
-
- Valish AU, Boyd NJ. The role of computer assisted instruction in continuing education of registered nurses: an experimental study. Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing 1975;6(1):13‐32. - PubMed
Van de Steeg 2012 {published data only}
Van Stiphout 2015 {published data only}
-
- Stiphout FZ‐vR, Aarts JE, Koffijberg H, Klarenbeek‐deJonge E, Krulder M, Roes KC, et al. MEDUCATE trial: effectiveness of an intensive EDUCATional intervention for IT‐mediated MEDication management in the outpatient clinic ‐ study protocol for a cluster randomized controlled trial. Trials 2015;16:223. - PMC - PubMed
Veredas 2014 {published data only}
-
- Veredas FJ, Ruiz‐Bandera E, Villa‐Estrada F, Rufino‐González JF, Morente L. A web‐based e‐learning application for wound diagnosis and treatment. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine 2014;116(3):236‐48. - PubMed
Vidal‐Pardo 2013 {published data only}
-
- Vidal‐Pardo JI, Pérez‐Castro TR, López‐Álvarez XL, Santiago‐Pérez MI, García‐Soidán FJ, Muñiz J. Effect of an educational intervention in primary care physicians on the compliance of indicators of good clinical practice in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus [OBTEDIGA project]. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2013;67(8):750‐8. - PubMed
Viguier 2015 {published data only}
Wakefield 2014 {published data only}
-
- Wakefield PL, Wilson MA. Enhancing nurses' knowledge regarding the complex care of hospitalised patients on insulin. Journal for Nurses in Professional Development 2014;30(4):174‐80. - PubMed
Ward 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ward L. E‐learning versus workshops to teach critical appraisal to health professionals: a randomised controlled equivalence study. Third International Evidence‐Based Librarianship Conference. 2005 Oct 16‐19, Brisbane, Australia2005.
Weaver 2012 {published data only}
Wehrs 2007 {published data only}
-
- Wehrs WH, Pfafflin M, May TW. E‐learning courses in epilepsy—concept, evaluation, and experience with the E‐learning course "genetics of epilepsies". Epilepsia 2007;48(5):872‐9. - PubMed
Weston 2008 {published data only}
-
- Weston CM, Sciamanna CN, Nash DB. Evaluating online continuing medical education seminars: evidence for improving clinical practices. American Journal of Medical Quality 2008;23(6):475‐83. - PubMed
Worm 2013 {published data only}
Yao 2015 {published data only}
References to studies awaiting assessment
Vollmar 2010 {published data only}
Additional references
Banzi 2009
-
- Banzi R, Moschetti I, Moja L. Internet‐based education for health professionals. JAMA 2009; Vol. 301, issue 6:599; author reply 599‐600. [PUBMED: 19211464] - PubMed
Borenstein 2009
-
- Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JPT, Rothstein HR. Introduction to Meta‐Analysis. 1st Edition. Chichester, West Sussex, UK: John Wiley & Sons Ltd., 2009.
Brendsen 2016 [pers comm]
-
- Bredesen IM. Re: Info Cochrane Review [personal communication]. Email to: A Vaona. 1 August 2016.
Cabana 2015 [pers comm]
-
- Cabana M. Re: Cochrane Review Info [personal communication]. Email to: A Vaona. 15 July 2015.
Chan 2004
-
- Chan AW, Hrobjartsson A, Haahr MT, Gotzsche PC, Altman DG. Empirical evidence for selective reporting of outcomes in randomised trials: comparison of protocols to published articles. JAMA 2004;291(20):2457‐2465. - PubMed
Chumley‐Jones 2002
-
- Chumley‐Jones HS, Dobbie A, Alford CL. Web‐based learning: sound educational method or hype? A review of the evaluation literature. Academic Medicine 2002;77(10) Suppl:S86‐S93. - PubMed
Clark 2011
-
- Clark RC, Mayer RE. E‐learning and the Science of Instruction: Proven Guidelines for Consumers and Designers of MultimediaLearning. 3rd Edition. San Francisco: John Wiley & Sons, 2011.
Cohen 1988
-
- Cohen J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences. 2nd Edition. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum, 1988.
Cook 2007
Cook 2008a
-
- Cook DA, Levinson AJ, Garside S, Dupras DM, Erwin PJ, Montori VM. Internet‐based learning in the health professions: a meta‐analysis. JAMA 2008;300(10):1181‐96. - PubMed
Cook 2008b
-
- Cook DA, McDonald FS. E‐learning: is there anything special about the "E"?. Perspectives in Biology and Medicine 2008;51(1):5‐21. - PubMed
Cook 2010a
-
- Cook DA, Levinson AJ, Garside S, Dupras DM, Erwin PJ, Montori VM. Instructional design variations in Internet‐based learning for health professions education: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Academic Medicine 2010;85:909‐22. - PubMed
Cook 2010b
-
- Cook DA, Garside S, Levinson AJ, Dupras DM, Montori VM. What do we mean by web‐based learning? A systematic review of the variability of interventions. Medical education 2010;44(8):765‐74. - PubMed
Cook 2010c
-
- Cook DA, Levinson AJ, Garside S. Time and learning efficiency in Internet‐based learning: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Advances in Health Sciences Education Theory and Practice 2010;15(5):755‐70. - PubMed
Coppus 2007
Deeks 2011
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available at www.cochrane‐handbook.org. Chichester (UK): John Wiley&Sons.
Dwan 2008
Egger 1997
Elbourne 2002
-
- Elbourne DR, Altman DA, Higgins JP, Curtin F, Worthington HV, Vail A. Meta‐analyses involving cross‐over trials: methodological issues. International Journal of Epidemiology 2002;31(1):140‐9. - PubMed
EPOC 2002
-
- Effective Practice, Organisation of Care (EPOC). EPOC Taxonomy. Oslo: Norwegian Knowledge Centre for the Health Services, 2002. Available from epoc.cochrane.org/epoc‐taxonomy.
EPOC 2013a
-
- Effective Practice, Organisation of Care (EPOC). What study designs should be included in an EPOC review and what should they be called? EPOC Resources for review authors. Oslo: Norwegian Knowledge Centre for the Health Services, 2013. Available from epocoslo.cochrane.org/epoc‐specific‐resources‐review‐authors.
EPOC 2013b
-
- Effective Practice, Organisation of Care (EPOC). Suggested risk of bias criteria for EPOC reviews. EPOC Resources for review authors. Oslo: Norwegian Knowledge Centre for the Health Services, 2013. Available from epoc.cochrane.org/epoc‐specific‐resources‐review‐authors.
EPOC 2015
-
- Effective Practice, Organisation of Care (EPOC). Data extraction and management. EPOC Resources for review authors. Oslo: Norwegian Knowledge Centre for the Health Services, 2015. Available from epoc.cochrane.org/epoc‐specific‐resources‐review‐authors.
Esche 2015 [pers comm]
-
- Esche C. Re: Info Cochrane Review [personal communication]. Email to: A Vaona. 27 July 2015.
Gibbons 2000
-
- Gibbons A, Fairweather P. Computer‐based instruction. In: Tobias S, Fletcher J editor(s). Training & Retraining: A Handbook for Business, Industry, Government, and the Military. New York: Macmillan Reference USA, 2000.
Glen 2005
-
- Glen ND. Cohort Analysis (Quantitative Applications in the Social Sciences). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005.
GRADEpro 2008 [Computer program]
-
- Brozek J, Oxman A, Schünemann H. GRADEpro. Version 3.2 for Windows. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime), 2008.
Harbord 2006
-
- Harbord RM, Egger M, Sterne JA. A modified test for small‐study effects in meta‐analyses of controlled trials with binary endpoints. Statistics in Medicine 2006;25:344‐57. - PubMed
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ (editors). Higgins JPT, Green S (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available at www.cochrane‐handbook.org. Chichester (UK): John Wiley&Sons.
Higgins 2011b
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available at www.cochrane‐handbook.org. Chichester (UK): John Wiley&Sons.
Jason 2015 [pers comm]
-
- Jason K. Re: Info Cochrane Review [personal communication]. Email to: A Vaona and Fordis CM Jr. 17 August 2015.
Kemper 2015 [pers comm]
-
- Kemper K. Re: Info Cochrane Review [personal communication]. Email to: A Vaona. 12 April 2015.
Kimani 2015 [pers comm]
-
- Kimani P. Re: Info Cochrane Review [personal communication]. Email to A Vaona and G Perkins. 17 August 2015.
Kirkham 2010
-
- Kirkham JJ, Dwan KM, Altman DG, Gamble C, Dodd S, Smyth R, et al. The impact of outcome reporting bias in randomised controlled trials on a cohort of systematic reviews. BMJ 2010;340:c365. - PubMed
Kirkpatrick 1996
-
- Kirkpatrick DL. Revisiting Kirkpatrick's four‐level‐model. Training & Development 1996;1:54‐7.
Kontio 2015 [pers comm]
-
- Kontio R. Re: Info Cochrane Review [personal communication]. Email to: A Vaona. 16 August 2015.
Lahti 2014
-
- Lahti M, Hätönen H, Välimäki M. Impact of e‐learning on nurses' and student nurses knowledge, skills, and satisfaction: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. International Journal of Nursing Studies 2014;51(1):136‐49. - PubMed
Lalonde 2015 [pers comm]
-
- Lalonde L. Re: Info Cochrane Review [personal communication]. Email to: A Vaona 13 April 2015.
Lam‐Antoniades 2009
-
- Lam‐Antoniades M, Ratnapalan S, Tait G. Electronic continuing education in the health professions: an update on evidence from RCTs. Journal of Continuing Education in the Health Professions 2009;29(1):44‐51. [PUBMED: 19288566] - PubMed
Li 2009
-
- Li LC, Moja L, Romero A, Sayre EC, Grimshaw JM. Nonrandomized quality improvement intervention trials might overstate the strength of causal inference of their findings. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2009;62(9):959‐66. [PUBMED: 19211223] - PubMed
Liaw 2016 [pers comm]
-
- Liaw SY. Re: Info from your trial for a Cochrane Review [personal communication]. Email to: A Vaona. 18 July 2016.
Liberati 2009
Menon 2012
-
- Menon A, Korner‐Bitensky N, Chignell M, Straus S. Usability testing of two e‐learning resources: methods to maximize potential for clinician use. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2012;44(4):338‐45. - PubMed
Miller 1990
-
- Miller GE. The assessment of clinical skills/competence/performance. Academic Medicine 1990;65:S63‐67. - PubMed
Moja 2007
Moja 2014
-
- Moja L, Pecoraro V, Ciccolallo L, Dall'Olmo L, Virgili G, Garattini S. Flaws in animal studies exploring statins and impact on meta‐analysis. European Journal of Clinical Investigation 2014;44(6):597‐612. - PubMed
Pelayo‐Alvarez 2015 [pers comm]
-
- Pelayo‐Alvarez M. Re: Info Cochrane Review [personal communication]. Email to: A Vaona. 14 October 2015.
Pham 2016 [pers comm]
-
- Pham D. Re: Info from your trial for a Cochrane Review [personal communication]. Email to: A Vaona. 18 July 2016.
Poon 2015
Rethans 2002
-
- Rethans JJ, Norcini JJ, Baron‐Maldonado M, Blackmore D, Jolly BC, LaDuca T, et al. The relationship between competence and performance: implications for assessing practice performance. Medical Education 2002;36:901‐9. - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Ruiz 2006
-
- Ruiz JG, Mintzer MJ, Leipzing RM. The impact of e‐learning in medical education. Academic Medicine 2006;81(3):207‐12. - PubMed
Ruiz 2007
-
- Ruiz JG, Teasdale TA, Hajjar I, Shaughnessy M, Mintzer MJ. The consortium of e‐learning in geriatrics instruction. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2007;55(3):458‐63. - PubMed
Savovic 2012
-
- Savović J, Jones H, Altman D, Harris R, Jűni P, Pildal J, et al. Influence of reported study design characteristics on intervention effect estimates from randomised controlled trials: combined analysis of meta‐epidemiological studies. Health Technology Assessment 2012;16(35):1‐82. - PubMed
Schünemann 2011
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, et al. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011 Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Sinclair 2016
-
- Sinclair PM, Kable A, Levett‐Jones T, Booth D. The effectiveness of Internet‐based e‐learning on clinician behaviour and patient outcomes: a systematic review. International Journal of Nursing Studies 2016;57:70‐81. - PubMed
Straus 2004
University of Aberdeen 2015
-
- University of Aberdeen, Health Services Research Unit. Database of intra‐correlation coefficients (ICCs). 2005. www.abdn.ac.uk/hsru/research/delivery/behaviour/methodological‐research (accessed prior to 19 December 2017).
Virgili 2009
-
- Virgili G, Conti AA, Moja L, Gensini GF, Gusinu R. Heterogeneity and meta‐analyses: do study results truly differ?. Internal and Emergency Medicine 2009;4(5):423‐7. - PubMed
Ward 2001
-
- Ward JP, Gordon J, Field MJ, Lehmann HP. Communication and information technology in medical education. Lancet 2001;357(9258):792‐6. - PubMed
Weijer 2012
Welsh 2003
-
- Welsh ET, Wanberg CR, Brown KG, Simmering MJ. E‐learning: emerging uses, empirical results and future directions. International Journal of Training and Development 2003;7(4):245‐58.
Wentling 2000
-
- Wentling TL, Waight C, Gallagher J, Fleur J, Wang C, Kanfer A. E‐learning ‐ a review of literature. University of Illinois at Urbana‐Champaign, 2000. learning.ncsa.uiuc.edu/papers/elearnlit.pdf (accessed prior to 19 December 2017).
Wood 2008
Wutoh 2004
-
- Wutoh R, Boren SA, Balas EA. eLearning: a review of Internet‐based continuing medical education. Journal of Continuing Education in the Health Professions 2004;24(1):20‐30. - PubMed
Zimitat 2001
-
- Zimitat C. Designing effective on‐line continuing medical education. Medical Teacher 2001;23(2):117‐22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

