Hallucinations, neuroplasticity, and prediction errors in schizophrenia
- PMID: 29356009
- PMCID: PMC5969574
- DOI: 10.1111/sjop.12413
Hallucinations, neuroplasticity, and prediction errors in schizophrenia
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum.Scand J Psychol. 2018 Jun;59(3):349. doi: 10.1111/sjop.12456. Scand J Psychol. 2018. PMID: 29733449 No abstract available.
Abstract
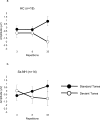
Auditory hallucinations, a hallmark symptom of psychosis, are experienced by most people with a diagnosis of schizophrenia at some point in their illness. Auditory hallucinations can be understood as a failure in predictive coding, whereby abnormalities in sensory/perceptual processing combine with biased cognitive processes to result in a dampening of normal prediction error signaling. In this paper, we used a roving mismatch negativity (MMN) paradigm to optimize evaluation of prediction error signaling and short-term neuroplasticity in 30 people with schizophrenia (n = 16 with and n = 14 without recent auditory hallucinations) and 20 healthy comparison participants. The recent hallucinations group exhibited an abnormal roving MMN profile [F(2,27) = 3.98, p = 0.03], significantly reduced prediction error signaling [t(28) = -2.25, p = 0.03], and a trend for diminished short-term neuroplasticity [t(28) = 1.80, p = 0.08]. There were no statistically significant differences between the healthy comparison group and the combined schizophrenia group on any of the roving MMN indices. These findings are consistent with a predictive coding account of hallucinations in schizophrenia, which posits reduced prediction error signaling in those who are prone to hallucinations. These results also suggest that plasticity-mediated formation and online updating of predictive coding models may also be disrupted in individuals with recent hallucinations.
Keywords: Auditory hallucinations; mismatch negativity; prediction error signaling; psychotic disorders; roving MMN; short-term neuroplasticity.
© 2018 Scandinavian Psychological Associations and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4th. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1994. (DSM-IV)
-
- Baker CA, Morrison AP. Cognitive processes in auditory hallucinations: attributional biases and metacognition. Psychological Medicine. 1998;28(5):1199–208. - PubMed
-
- Baldeweg T. ERP Repetition Effects and Mismatch Negativity Generation A Predictive Coding Perspective. ERP Repetition Ef Fects and Mismatch Negativity Generation Journal of Psychophysiology. 2007;21 http://doi.org/10.1027/0269-8803.21.34.204. - DOI
-
- Baldeweg T, Hirsch SR. Mismatch negativity indexes illness-specific impairments of cortical plasticity in schizophrenia: a comparison with bipolar disorder and Alzheimer’s disease. International Journal of Psychophysiology. 2015;95(2):145–155. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2014.03.008. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baldeweg T, Klugman A, Gruzelier J, Hirsch SR. Mismatch negativity potentials and cognitive impairment in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research. 2004;69(2–3):203–217. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2003.09.009. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

