Kisspeptin neurones in the posterodorsal medial amygdala modulate sexual partner preference and anxiety in male mice
- PMID: 29356147
- PMCID: PMC5873280
- DOI: 10.1111/jne.12572
Kisspeptin neurones in the posterodorsal medial amygdala modulate sexual partner preference and anxiety in male mice
Abstract
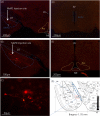
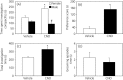
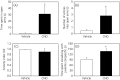
The posterodorsal medial amygdala (MePD) is a neural site in the limbic brain involved in regulating emotional and sexual behaviours. There is, however, limited information available on the specific neuronal cell type in the MePD functionally mediating these behaviours in rodents. The recent discovery of a significant kisspeptin neurone population in the MePD has raised interest in the possible role of kisspeptin and its cognate receptor in sexual behaviour. The present study therefore tested the hypothesis that the MePD kisspeptin neurone population is involved in regulating attraction towards opposite sex conspecifics, sexual behaviour, social interaction and the anxiety response by selectively stimulating these neurones using the novel pharmacosynthetic DREADDs (designer receptors exclusively activated by designer drugs) technique. Adult male Kiss-Cre mice received bilateral stereotaxic injections of a stimulatory DREADD viral construct (AAV-hSyn-DIO-hM3 D(Gq)-mCherry) targeted to the MePD, with subsequent activation by i.p. injection of clozapine-N-oxide (CNO). Socio-sexual behaviours were assessed in a counter-balanced fashion after i.p. injection of either saline or CNO (5 mg kg-1 ). Selective activation of MePD kisspeptin neurones by CNO significantly increased the time spent by male mice in investigating an oestrous female, as well as the duration of social interaction. Additionally, after CNO injection, the mice appeared less anxious, as indicated by a longer exploratory time in the open arms of the elevated plus maze. However, levels of copulatory behaviour were comparable between CNO and saline-treated controls. These data indicate that DREADD-induced activation of MePD kisspeptin neurones enhances both sexual partner preference in males and social interaction and also decreases anxiety, suggesting a key role played by MePD kisspeptin in sexual motivation and social behaviour.
Keywords: amygdala; anxiety; kisspeptin; mice; partner preference; sexual behaviour.
© 2018 The Authors. Journal of Neuroendocrinology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Society for Neuroendocrinology.
Figures
References
-
- Lehman MN, Winans SS. Vomeronasal and olfactory pathways to the amygdala controlling male hamster sexual behavior: autoradiographic and behavioral analyses. Brain Res. 1982;240:27‐41. - PubMed
-
- Oberlander JG, Erskine MS. Receipt of vaginal‐cervical stimulation modifies synapsin content in limbic areas of the female rat. Neuroscience. 2008;153:581‐593. - PubMed
-
- Kollack‐Walker S, Newman SW. Mating and agonistic behavior produce different patterns of Fos immunolabeling in the male Syrian hamster brain. Neuroscience. 1995;66:721‐736. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

