Architecture of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Replisome
- PMID: 29357060
- PMCID: PMC5800748
- DOI: 10.1007/978-981-10-6955-0_10
Architecture of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Replisome
Abstract
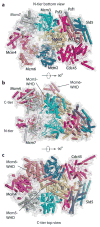
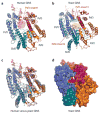
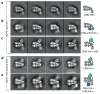
Eukaryotic replication proteins are highly conserved, and thus study of Saccharomyces cerevisiae replication can inform about this central process in higher eukaryotes including humans. The S. cerevisiae replisome is a large and dynamic assembly comprised of ~50 proteins. The core of the replisome is composed of 31 different proteins including the 11-subunit CMG helicase; RFC clamp loader pentamer; PCNA clamp; the heteroligomeric DNA polymerases ε, δ, and α-primase; and the RPA heterotrimeric single strand binding protein. Many additional protein factors either travel with or transiently associate with these replisome proteins at particular times during replication. In this chapter, we summarize several recent structural studies on the S. cerevisiae replisome and its subassemblies using single particle electron microscopy and X-ray crystallography. These recent structural studies have outlined the overall architecture of a core replisome subassembly and shed new light on the mechanism of eukaryotic replication.
Keywords: CMG; Cryo-EM; DNA polymerase; Eukaryotic DNA replication; Mcm; Replicative helicase; Replisome; Structural biology.
Figures


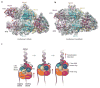


References
-
- Asturias FJ, Cheung IK, Sabouri N, Chilkova O, Wepplo D, Johansson E. Structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA polymerase epsilon by cryo-electron microscopy. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006;13:35–43. - PubMed
-
- Banks GR, Boezi JA, Lehman IR. A high molecular weight DNA polymerase from Drosophila melanogaster embryos. Purification, structure, and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1979;254:9886–9892. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

