The mortality risk factor of community acquired pneumonia patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 29357862
- PMCID: PMC5778745
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-018-0587-7
The mortality risk factor of community acquired pneumonia patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is one of the most common comorbidities in community acquired pneumonia (CAP) patients. We aimed to investigate the characteristics and mortality risk factors of COPD patients hospitalized with CAP.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted at Shanghai Pulmonary Hospital and Shanghai Dahua Hospital. Clinical and demographic data in patients diagnosed with CAP were collected between January 2015 and June 2016. Logistic regression analysis was performed to screen mortality risk factors of COPD patients hospitalized with CAP.
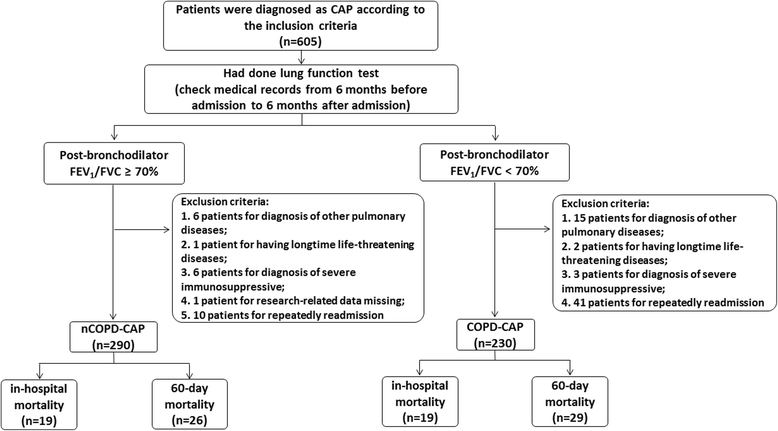
Results: Of the total 520 CAP patients, 230 (44.2%) patients had been diagnosed comorbid with COPD (COPD-CAP). CAP patients comorbid with COPD patients had higher rate of need for ICU admission (18.3% vs 13.1%) and need for NIMV (26.1% vs 1.4%) than without COPD (nCOPD-CAP). The PSI, CURB-65 and APACHE-II scores in COPD-CAP patients were higher than that in nCOPD-CAP patients (95 vs 79, P < 0.001; 1 vs 1, P < 0.001; 13 vs 8, P < 0.001, respectively). Logistic regression analysis indicated that aspiration, D-dimer > 2.0 μg/mL and CURB-65 ≥ 3 were risk factors associated with in-hospital mortality ((odd ratio) OR = 5.678, OR = 4.268, OR = 20.764, respectively) in COPD-CAP patients. The risk factors associated with 60-day mortality in COPD-CAP patients were comorbid with coronary heart disease, aspiration, need for NIMV (non-invasive mechanical ventilation) and CURB-65 ≥ 3 (OR = 5.206, OR = 7.921, OR = 3.974, OR = 18.002, respectively).
Conclusions: COPD patients hospitalized with CAP had higher rate of need for NIMV, need for ICU admission and severity scores than those without COPD. Aspiration, D-dimer > 2.0 μg/mL, comorbid with coronary heart disease, need for NIMV and CURB-65 ≥ 3 were mortality risk factors in CAP patients comorbid with COPD.
Keywords: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; Community acquired pneumonia; Mortality; Severity scoring systems.
Conflict of interest statement
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
-
- Mandell LA, Wunderink RG, Anzueto A, Bartlett JG, Campbell GD, Dean NC, et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America/American Thoracic Society consensus guidelines on the management of community-acquired pneumonia in adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44(Suppl 2):S27–S72. doi: 10.1086/511159. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous