Comparative efficacy and acceptability of antiepileptic drugs for classical trigeminal neuralgia: a Bayesian network meta-analysis protocol
- PMID: 29358420
- PMCID: PMC5780694
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-017392
Comparative efficacy and acceptability of antiepileptic drugs for classical trigeminal neuralgia: a Bayesian network meta-analysis protocol
Abstract
Introduction: Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) affects 4 to 28.9/100 000 people worldwide, and antiepileptic drugs such as carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine are the firstline treatment options. However, the efficacy and safety of other antiepileptic drugs remain unclear due to insufficient direct comparisons.
Objective: To compare the efficacy and acceptability of all currently available antiepileptic agents for the treatment of patients with classical TN.
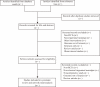
Methods: We will search the PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library and Web of Science databases for unpublished or undergoing research listed in registry platforms. We will include all randomised controlled trials comparing two different antiepileptic drugs or one antiepileptic drug with placebo in patients with classical TN. The primary outcomes will be the proportion of responders and the number of subjects who dropout during the treatment. The secondary outcomes will include the two primary outcomes but in the follow-up period, changes in the self-reporting assessment scale for neuralgia and quality of life assessment. In terms of network meta-analysis, we will fit our model to a Bayesian framework using the JAGS and pcnetmeta packages of the R project.
Ethics and dissemination: This protocol will not disseminate any private patient data. The results of this review will be disseminated through peer reviewed publication.
Prospero registration number: CRD42016048640.
Keywords: antiepileptic drugs; network meta-analysis; protocol; systematic review; trigeminal neuralgia.
© Article author(s) (or their employer(s) unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2018. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antiepileptic drug monotherapy for epilepsy: a network meta-analysis of individual participant data.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Apr 1;4(4):CD011412. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011412.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35363878 Free PMC article.
-
Non-antiepileptic drugs for trigeminal neuralgia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Dec 3;2013(12):CD004029. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004029.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 24297506 Free PMC article.
-
Antiepileptic drugs for chronic non-cancer pain in children and adolescents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Aug 5;8(8):CD012536. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012536.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28779491 Free PMC article.
-
Antiepileptic drug monotherapy for epilepsy: a network meta-analysis of individual participant data.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 15;12(12):CD011412. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011412.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Apr 1;4:CD011412. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011412.pub4. PMID: 29243813 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Antiepileptic drug monotherapy for epilepsy: a network meta-analysis of individual participant data.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 29;6(6):CD011412. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011412.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 15;12:CD011412. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011412.pub3. PMID: 28661008 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy across chronic pain disorders: a systematic review protocol synthesising anatomical and metabolite findings in chronic pain patients.Syst Rev. 2019 Dec 27;8(1):338. doi: 10.1186/s13643-019-1256-5. Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31882014 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture therapy for change of pain in classical trigeminal neuralgia.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Apr;99(16):e19710. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019710. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32311955 Free PMC article.
-
Oral pharmacological treatments for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.EClinicalMedicine. 2022 May 20;48:101457. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101457. eCollection 2022 Jun. EClinicalMedicine. 2022. PMID: 35706494 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the comparative efficacy and tolerability of comprehensive treatments for migraine: A protocol of systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Jan 29;100(4):e24083. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000024083. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33530202 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Percutaneous Ozone Injection Around Gasserian Ganglion for the Treatment of Trigeminal Neuralgia: A Multicenter Retrospective Study.J Pain Res. 2020 May 4;13:927-936. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S232081. eCollection 2020. J Pain Res. 2020. PMID: 32440198 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical