Ex Vivo Tracer Efficacy in Optical Imaging of Staphylococcus Aureus Nuclease Activity
- PMID: 29358617
- PMCID: PMC5778018
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-19289-y
Ex Vivo Tracer Efficacy in Optical Imaging of Staphylococcus Aureus Nuclease Activity
Abstract
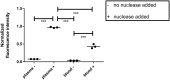
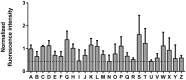
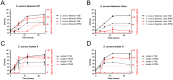
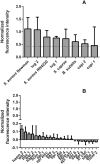
The key to effective treatment of bacterial infections is a swift and reliable diagnosis. Current clinical standards of bacterial diagnosis are slow and laborious. There are several anatomical imaging modalities that can detect inflammation, but none can distinguish between bacterial and sterile inflammation. Novel tracers such as smart activatable fluorescent probes represent a promising development that allow fast and specific testing without the use of ionizing radiation. Previously, a smart activatable probe was developed that is a substrate for the micrococcal nuclease as produced by Staphylococcus aureus. In the present study, the function of this probe was validated. Practical applicability in terms of sensitivity was assessed by incubation of the probe with 26 clinical S. aureus isolates, and probe specificity was verified by incubation with 30 clinical isolates and laboratory strains of various bacterial pathogens. The results show that the nuclease-specific probe was activated by all tested S. aureus isolates and laboratory strains with a threshold of ~106-107 cells/mL. The probe was also activated by certain opportunistic staphylococci. We therefore propose that the studied nuclease probe represents a significant step forward to address the need for a rapid, practical, and precise method to detect infections caused by S. aureus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Annual epidemiological report 2014. Antimicrobial resistance and healthcare-associated infections. Available at: http://ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications/Publications/antimicrobial-resista... (Accessed 25 May 2016) (2015).
-
- Carek PJ, Dickerson LM, Sack JL. Diagnosis and management of osteomyelitis. Am. Fam. Physician. 2011;65:1751. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

