TLR3 Mediates Repair and Regeneration of Damaged Neonatal Heart through Glycolysis Dependent YAP1 Regulated miR-152 Expression
- PMID: 29358670
- PMCID: PMC5943401
- DOI: 10.1038/s41418-017-0036-9
TLR3 Mediates Repair and Regeneration of Damaged Neonatal Heart through Glycolysis Dependent YAP1 Regulated miR-152 Expression
Abstract
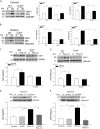
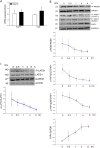
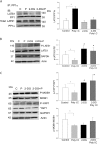
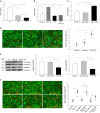
The present study investigated whether TLR3 is required for neonatal heart repair and regeneration following myocardial infarction (MI). TLR3 deficient neonatal mice exhibited impaired cardiac functional recovery and a larger infarct size, while wild type neonatal mice showed cardiac functional recovery and small infarct size after MI. The data suggest that TLR3 is essential for the regeneration and repair of damaged neonatal myocardium. In vitro treatment of neonatal cardiomyocytes with a TLR3 ligand, Poly (I:C), significantly enhances glycolytic metabolism, YAP1 activation and proliferation of cardiomyocytes which were prevented by a glycolysis inhibitor, 2-deoxyglucose (2-DG). Administration of 2-DG to neonatal mice abolished cardiac functional recovery and YAP activation after MI, suggesting that TLR3-mediated regeneration and repair of the damaged neonatal myocardium is through glycolytic-dependent YAP1 activation. Inhibition of YAP1 activation abolished Poly (I:C) induced proliferation of neonatal cardiomyocytes. Interestingly, activation of YAP1 increases the expression of miR-152 which represses the expression of cell cycle inhibitory proteins, P27kip1 and DNMT1, leading to cardiomyocyte proliferation. We conclude that TLR3 is required for neonatal heart regeneration and repair after MI. The mechanisms involve glycolytic-dependent YAP1 activation, resulting in miR-152 expression which targets DNMT1/p27kip1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing financial interests.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

