Stabilities of tocopherols and phenolic compounds in virgin olive oil during thermal oxidation
- PMID: 29358816
- PMCID: PMC5756209
- DOI: 10.1007/s13197-017-2929-5
Stabilities of tocopherols and phenolic compounds in virgin olive oil during thermal oxidation
Abstract
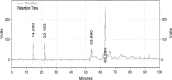
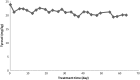
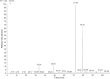
The effects of thermal oxidation at 60 °C on tocopherols (α, β, γ) and phenolic compounds (hydroxytyrosol and tyrosol) of olive oil were studied. Tocopherols were determined by HPLC and phenolic compounds by HPLC and GC-MS. Peroxide value of olive oil increased with treatment time until it reached to 56.6 meq/kg. α-Tocopherol, β-tocopherol and γ-tocopherol contents of olive oil decreased with treatment time. α-Tocopherol in olive oil was decomposed after 63 days of treatment. β-Tocopherol in olive oil was depleted after 33 days of treatment. The reduction in γ-tocopherol of olive oil was 75% after 63 days of treatment. The degradation of hydroxytyrosol in olive oil was 91% after 63 days of treatment. Tyrosol was more stable than hydroxytyrosol in olive oil. Inverse correlations of peroxide value with hydroxytyrosol, α-Tocopherol, β-tocopherol and γ-tocopherol were observed.
Keywords: Olive oil; Oxidation; Phenolic compound; Thermal treatment; Tocopherol.
Figures



References
-
- Arslan D, Karabekir Y, Schreiner M. Variations of phenolic compounds, fatty acids and some qualitative characteristics of Sarıulak olive oil as induced by growing area. Food Res Int. 2013;54:189–1906. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2013.06.016. - DOI
-
- Ballus CA, Meinhart AD, Campos FASJ, Silva LFO, Oliveira AF, Godoy HT. A quantitative study on the phenolic compound, tocopherol and fatty acid contents of monovarietal virgin olive oils produced in the southeast region of Brazil. Food Res Int. 2014;62:74–83. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2014.02.040. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
