Functional Modulation of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels by a FGF14-Based Peptidomimetic
- PMID: 29359916
- PMCID: PMC6033619
- DOI: 10.1021/acschemneuro.7b00399
Functional Modulation of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels by a FGF14-Based Peptidomimetic
Abstract
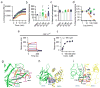
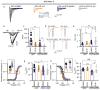
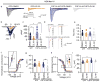
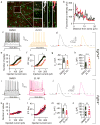
Protein-protein interactions (PPI) offer unexploited opportunities for CNS drug discovery and neurochemical probe development. Here, we present ZL181, a novel peptidomimetic targeting the PPI interface of the voltage-gated Na+ channel Nav1.6 and its regulatory protein fibroblast growth factor 14 (FGF14). ZL181 binds to FGF14 and inhibits its interaction with the Nav1.6 channel C-tail. In HEK-Nav1.6 expressing cells, ZL181 acts synergistically with FGF14 to suppress Nav1.6 current density and to slow kinetics of fast inactivation, but antagonizes FGF14 modulation of steady-state inactivation that is regulated by the N-terminal tail of the protein. In medium spiny neurons in the nucleus accumbens, ZL181 suppresses excitability by a mechanism that is dependent upon expression of FGF14 and is consistent with a state-dependent inhibition of FGF14. Overall, ZL181 and derivatives could lay the ground for developing allosteric modulators of Nav channels that are of interest for a broad range of CNS disorders.
Keywords: CNS drug discovery; Fibroblast growth factor 14 (FGF14); minimal functional domains; neurochemical probes; peptidomimetics; protein:protein interaction (PPI); voltage-gated sodium channels (Nav1.6).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
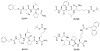

References
-
- Leterrier C, Brachet A, Fache MP, Dargent B. Voltage-gated sodium channel organization in neurons: protein interactions and trafficking pathways. Neurosci Lett. 2010;486:92–100. - PubMed
-
- Wildburger NC, Ali SR, Hsu WC, Shavkunov AS, Nenov MN, Lichti CF, LeDuc RD, Mostovenko E, Panova-Elektronova NI, Emmett MR, Nilsson CL, Laezza F. Quantitative proteomics reveals protein-protein interactions with fibroblast growth factor 12 as a component of the voltage-gated sodium channel 1.2 (nav1.2) macromolecular complex in Mammalian brain. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2015;14:1288–1300. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hu W, Tian C, Li T, Yang M, Hou H, Shu Y. Distinct contributions of Na(v)1.6 and Na(v)1.2 in action potential initiation and backpropagation. Nat Neurosci. 2009;12:996–1002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

