Distributed rhythm generators underlie Caenorhabditis elegans forward locomotion
- PMID: 29360037
- PMCID: PMC5780042
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.29913
Distributed rhythm generators underlie Caenorhabditis elegans forward locomotion
Abstract
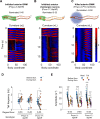
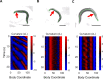
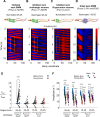
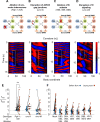
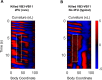
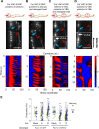
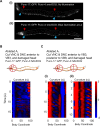
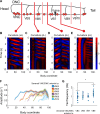
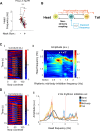
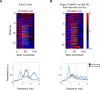
Coordinated rhythmic movements are ubiquitous in animal behavior. In many organisms, chains of neural oscillators underlie the generation of these rhythms. In C. elegans, locomotor wave generation has been poorly understood; in particular, it is unclear where in the circuit rhythms are generated, and whether there exists more than one such generator. We used optogenetic and ablation experiments to probe the nature of rhythm generation in the locomotor circuit. We found that multiple sections of forward locomotor circuitry are capable of independently generating rhythms. By perturbing different components of the motor circuit, we localize the source of secondary rhythms to cholinergic motor neurons in the midbody. Using rhythmic optogenetic perturbation, we demonstrate bidirectional entrainment of oscillations between different body regions. These results show that, as in many other vertebrates and invertebrates, the C. elegans motor circuit contains multiple oscillators that coordinate activity to generate behavior.
Keywords: C. elegans; CPG; behavior; locomotion; motor circuit; neuroscience; optogenetics; rhythm generator.
© 2017, Fouad et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AF, ST, JM, AL, PA, HJ, AD, PB, EC, SG, CF No competing interests declared
Figures






Similar articles
-
Excitatory motor neurons are local oscillators for backward locomotion.Elife. 2018 Jan 23;7:e29915. doi: 10.7554/eLife.29915. Elife. 2018. PMID: 29360035 Free PMC article.
-
Proprioceptive coupling within motor neurons drives C. elegans forward locomotion.Neuron. 2012 Nov 21;76(4):750-61. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.08.039. Neuron. 2012. PMID: 23177960 Free PMC article.
-
Functionally asymmetric motor neurons contribute to coordinating locomotion of Caenorhabditis elegans.Elife. 2018 Sep 11;7:e34997. doi: 10.7554/eLife.34997. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30204083 Free PMC article.
-
Caenorhabditis elegans excitatory ventral cord motor neurons derive rhythm for body undulation.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018 Sep 10;373(1758):20170370. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2017.0370. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30201835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
C. elegans locomotion: small circuits, complex functions.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2015 Aug;33:117-26. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2015.03.009. Epub 2015 Apr 4. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 25845627 Review.
Cited by
-
From head to tail: a neuromechanical model of forward locomotion in Caenorhabditis elegans.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018 Sep 10;373(1758):20170374. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2017.0374. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30201838 Free PMC article.
-
CKR-1 orchestrates two motor states from a single motoneuron in C. elegans.iScience. 2024 Mar 2;27(4):109390. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109390. eCollection 2024 Apr 19. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38510145 Free PMC article.
-
Thermal laser ablation with tunable lesion size reveals multiple origins of seizure-like convulsions in Caenorhabditis elegans.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 3;11(1):5084. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84516-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33658607 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive, locally linear models of complex dynamics.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Jan 29;116(5):1501-1510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1813476116. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30655347 Free PMC article.
-
Proprioception, the regulator of motor function.BMB Rep. 2021 Aug;54(8):393-402. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2021.54.8.052. BMB Rep. 2021. PMID: 34078529 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

