Multiple target autoantigens on endothelial cells identified in juvenile dermatomyositis using proteomics
- PMID: 29361142
- PMCID: PMC5888918
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kex468
Multiple target autoantigens on endothelial cells identified in juvenile dermatomyositis using proteomics
Abstract
Objective: Although generally classified within the group of inflammatory myopathies, JDM displays many pathological features of vasculitis. Previous work has shown that AECA are abundant in other forms of vasculitis. We therefore investigated whether such antibodies might also be detected in JDM.
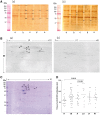
Methods: We screened plasma from children with JDM for the presence of AECA by western blotting and 2D gel electrophoresis (2DE) using proteins extracted from human aortic endothelial cells as the substrate. We performed mass spectrometry to identify candidate antigens from 2DE gels and used ELISA to confirm the presence of specific antibodies.
Results: We identified 22 candidate target autoantigens for AECA probed with JDM plasma. Interestingly, 17 of these 22 target antigens were proteins associated with antigen processing and protein trafficking. ELISA confirmed the presence of antibodies to heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein in JDM plasma, particularly in children with active, untreated disease.
Conclusion: Children with JDM express antibodies to autoantigens in endothelial cells. The clinical and pathological significance of such autoantibodies require further investigation.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

