Characterization of a novel RP2-OSTF1 interaction and its implication for actin remodelling
- PMID: 29361551
- PMCID: PMC5868953
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.211748
Characterization of a novel RP2-OSTF1 interaction and its implication for actin remodelling
Abstract
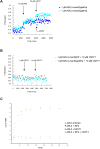
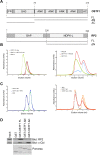
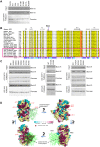
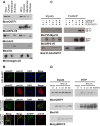
Retinitis pigmentosa 2 (RP2) is the causative gene for a form of X-linked retinal degeneration. RP2 was previously shown to have GTPase-activating protein (GAP) activity towards the small GTPase ARL3 via its N-terminus, but the function of the C-terminus remains elusive. Here, we report a novel interaction between RP2 and osteoclast-stimulating factor 1 (OSTF1), an intracellular protein that indirectly enhances osteoclast formation and activity and is a negative regulator of cell motility. Moreover, this interaction is abolished by a human pathogenic mutation in RP2. We utilized a structure-based approach to pinpoint the binding interface to a strictly conserved cluster of residues on the surface of RP2 that spans both the C- and N-terminal domains of the protein, and which is structurally distinct from the ARL3-binding site. In addition, we show that RP2 is a positive regulator of cell motility in vitro, recruiting OSTF1 to the cell membrane and preventing its interaction with the migration regulator Myo1E.
Keywords: Actin; OSTF1; RP2; Retinitis pigmentosa.
© 2018. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Chapple J. P., Hardcastle A. J., Grayson C., Spackman L. A., Willison K. R. and Cheetham M. E. (2000). Mutations in the N-terminus of the X-linked retinitis pigmentosa protein RP2 interfere with the normal targeting of the protein to the plasma membrane. Hum. Mol. Genet. 9, 1919-1926. 10.1093/hmg/9.13.1919 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chapple J. P., Hardcastle A. J., Grayson C., Willison K. R. and Cheetham M. E. (2002). Delineation of the plasma membrane targeting domain of the X-linked retinitis pigmentosa protein RP2. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 43, 2015-2020. - PubMed
-
- Chen L., Wang Y., Wells D., Toh D., Harold H., Zhou J., Digiammarino E. and Meehan E. J. (2006). Structure of the SH3 domain of human osteoclast-stimulating factor at atomic resolution. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 62, 844-848. 10.1107/S1744309106030004 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

