Elevated Aromatase (CYP19A1) Expression Is Associated with a Poor Survival of Patients with Estrogen Receptor Positive Breast Cancer
- PMID: 29363090
- PMCID: PMC5862917
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-017-0317-2
Elevated Aromatase (CYP19A1) Expression Is Associated with a Poor Survival of Patients with Estrogen Receptor Positive Breast Cancer
Abstract
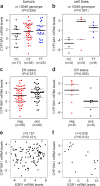
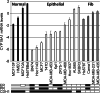
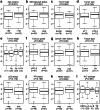
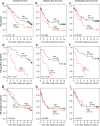
Genetic variants in CYP19A1, the gene encoding aromatase, have been reported to be associated with circulating estrogen concentrations, a key risk factor for breast cancer. The mechanism underlying this association is still unclear; it has been suggested that some of these variants may alter the expression and/or activity of aromatase. Here we analyzed the expression of intra-tumoral CYP19A1 messenger RNA (mRNA) and the genotypes of rs10046, a well-characterized single nucleotide polymorphism in CYP19A1, in 138 breast cancer patients and 15 breast cancer cell lines. The genotype TT was detected in 36 patients and six cell lines, genotype CT in 55 patients and five cell lines, and genotype CC in 28 patients and four cell lines. We found no evidence for a significant association of CYP19A1 levels with rs10046 genotypes, although expression tended to be higher in tumors and cell lines with the homozygous risk genotype TT. We also found no evidence for a significant association of rs10046 genotypes with breast cancer prognosis. In contrast, high CYP19A1 expression was highly significantly associated with a poor overall, disease-free, and metastasis-free survival in estrogen receptor-positive but not negative breast cancer patients. Moreover, CYP19A1 mRNA was significantly elevated in postmenopausal patients and in patients older than 50 years, and a trend towards a positive correlation with ER status and ESR1 mRNA expression was observed. These findings highlight the key role of aromatase in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CYP19A1 polymorphisms and clinical outcomes in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer in the BIG 1-98 trial.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015 Jun;151(2):373-84. doi: 10.1007/s10549-015-3378-3. Epub 2015 May 3. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015. PMID: 25935582 Free PMC article.
-
Single nucleotide polymorphisms of the aromatase gene (CYP19A1), HER2/neu status, and prognosis in breast cancer patients.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008 Nov;112(1):89-98. doi: 10.1007/s10549-007-9822-2. Epub 2007 Nov 30. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008. PMID: 18049890
-
CYP19A1 rs10046 Pharmacogenetics in Postmenopausal Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Aromatase Inhibitors: One-year Follow-up.Curr Pharm Des. 2020;26(46):6007-6012. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666200908141858. Curr Pharm Des. 2020. PMID: 32900345
-
Association between rs10046, rs1143704, rs767199, rs727479, rs1065778, rs1062033, rs1008805, and rs700519 polymorphisms in aromatase (CYP19A1) gene and Alzheimer's disease risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis involving 11,051 subjects.Neurol Sci. 2019 Dec;40(12):2515-2527. doi: 10.1007/s10072-019-04003-1. Epub 2019 Jul 5. Neurol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31278540
-
Transcriptional control of local estrogen formation by aromatase in the breast.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015 Jan;145:179-86. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2014.05.004. Epub 2014 May 17. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 24846828 Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of CYP19A1 variants and haplotypes on breast cancer risk, clinicopathological features and prognosis.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2021 Jul;9(7):e1705. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1705. Epub 2021 May 20. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2021. PMID: 34014013 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoplasmic PPARγ is a marker of poor prognosis in patients with Cox-1 negative primary breast cancers.J Transl Med. 2020 Feb 21;18(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02271-6. J Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32085795 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology integrated with molecular docking reveals the anticancer mechanism of Jasminum sambac Linn. essential oil against human breast cancer and experimental validation by in vitro and in vivo studies.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024 Jan;196(1):350-381. doi: 10.1007/s12010-023-04481-2. Epub 2023 May 2. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37129744
-
Association of the MDM2 SNP285 and SNP309 Genetic Variants with the Risk, Age at Onset and Prognosis of Breast Cancer in Central European Women: A Hospital-Based Case-Control Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 25;20(3):509. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030509. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30691044 Free PMC article.
-
The 40bp Indel Polymorphism rs150550023 in the MDM2 Promoter is Associated with Intriguing Shifts in Gene Expression in the p53-MDM2 Regulatory Hub.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Nov 13;12(11):3363. doi: 10.3390/cancers12113363. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33202864 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaaks R, Rinaldi S, Key TJ, Berrino F, Peeters PH, Biessy C, Dossus L, Lukanova A, Bingham S, Khaw KT, Allen NE, Bueno-de-Mesquita HB, van Gils CH, Grobbee D, Boeing H, Lahmann PH, Nagel G, Chang-Claude J, Clavel-Chapelon F, Fournier A, Thiebaut A, Gonzalez CA, Quiros JR, Tormo MJ, Ardanaz E, Amiano P, Krogh V, Palli D, Panico S, Tumino R, Vineis P, Trichopoulou A, Kalapothaki V, Trichopoulos D, Ferrari P, Norat T, Saracci R, Riboli E. Postmenopausal serum androgens, oestrogens and breast cancer risk: the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005;12:1071–1082. doi: 10.1677/erc.1.01038. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

