Linc-RAM is required for FGF2 function in regulating myogenic cell differentiation
- PMID: 29364044
- PMCID: PMC5927723
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2018.1431494
Linc-RAM is required for FGF2 function in regulating myogenic cell differentiation
Abstract
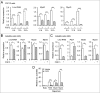
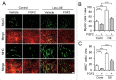
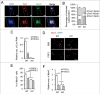
Myogenic differentiation of skeletal muscle stem cells, also known satellite cells, is tightly orchestrated by extrinsic and intrinsic regulators. Basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF2) is well documented to be implicated in satellite cell self-renewal and differentiation by repressing MyoD. We recently identified a MyoD-regulated and skeletal muscle-specifically expressed long non-coding RNA Linc-RAM which enhances myogenic differentiation by facilitating MyoD/Baf60c/Brg1 complex assembly. Herein, we investigated the transcriptional regulation and intracellular signaling pathway in mediating Linc-RAM gene expression during muscle cell differentiation. Firstly, we demonstrate Linc-RAM is negatively regulated by FGF2 via Ras/Raf/Mek/Erk signaling pathway in muscle cells. Overexpression of MyoD significantly attenuates repression of Linc-RAM promoter activities in C2C12 cells treated with FGF2. Knockout of MyoD abolishes FGF2-mediated repression of Linc-RAM gene transcription in satellite cells sorted from skeletal muscle of MyoD-/-;Pax7-nGFP mice, suggesting inhibition of MyoD is required for FGF2-mediated expression of Linc-RAM. For the functional significance, we show that overexpression of Linc-RAM rescues FGF2-induced inhibition of C2C12 cell differentiation, indicating inhibition of Linc-RAM is required for FGF2-mediated suppression of myogenic differentiation. Consistently, we are able to further corroborate the requirement of Linc-RAM inhibition for FGF2-modulated repression of myogenic differentiation by using an ex vivo cultured single fiber system and satellite cells sorted from Linc-RAM-/-;Pax7-nGFP knockout mice. Collectively, the present study not only reveals the intracellular signaling in FGF2-mediated Linc-RAM gene expression but also demonstrate the functional significance of Linc-RAM in FGF2-mediated muscle cell differentiation.
Keywords: FGF2; Linc-RAM; Long non-coding RNA; MyoD; muscle cell differentiation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Long non-coding RNA Linc-RAM enhances myogenic differentiation by interacting with MyoD.Nat Commun. 2017 Jan 16;8:14016. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14016. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28091529 Free PMC article.
-
MyoD Over-Expression Rescues GST-bFGF Repressed Myogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 13;25(8):4308. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084308. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38673893 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of Linc-RNA activator of myogenesis lncRNA participates in FGF2-mediated proliferation of human periodontal ligament stem cells.J Periodontol. 2020 Mar;91(3):422-427. doi: 10.1002/JPER.19-0317. Epub 2019 Sep 11. J Periodontol. 2020. PMID: 31378921
-
Defining the transcriptional signature of skeletal muscle stem cells.J Anim Sci. 2008 Apr;86(14 Suppl):E207-16. doi: 10.2527/jas.2007-0473. Epub 2007 Sep 18. J Anim Sci. 2008. PMID: 17878281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The molecular regulation of muscle stem cell function.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2008;73:323-31. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2008.73.064. Epub 2009 Mar 27. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2008. PMID: 19329572 Review.
Cited by
-
Long noncoding RNA lncMREF promotes myogenic differentiation and muscle regeneration by interacting with the Smarca5/p300 complex.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Oct 14;50(18):10733-10755. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac854. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 36200826 Free PMC article.
-
Stable Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 Dimers with High Pro-Survival and Mitogenic Potential.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 9;21(11):4108. doi: 10.3390/ijms21114108. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32526859 Free PMC article.
-
MEG3 Promotes Differentiation of Porcine Satellite Cells by Sponging miR-423-5p to Relieve Inhibiting Effect on SRF.Cells. 2020 Feb 15;9(2):449. doi: 10.3390/cells9020449. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32075310 Free PMC article.
-
New developments in the biology of fibroblast growth factors.WIREs Mech Dis. 2022 Jul;14(4):e1549. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.1549. Epub 2022 Feb 9. WIREs Mech Dis. 2022. PMID: 35142107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fibroblast Growth Factors: Roles and Emerging Therapeutic Applications.Curr Drug Targets. 2025;26(8):551-570. doi: 10.2174/0113894501351461250301072444. Curr Drug Targets. 2025. PMID: 40051360 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
