Marek's disease vaccine activates chicken macrophages
- PMID: 29366301
- PMCID: PMC5974519
- DOI: 10.4142/jvs.2018.19.3.375
Marek's disease vaccine activates chicken macrophages
Abstract
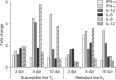
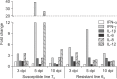
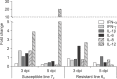
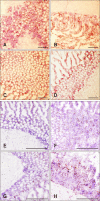
To provide insights into the role of innate immune responses in vaccine-mediated protection, we investigated the effect of Marek's disease (MD) vaccine, CVI988/Rispens, on the expression patterns of selected genes associated with activation of macrophages in MD-resistant and MD-susceptible chicken lines. Upregulation of interferon γ, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-8, and IL-12 at different days post-inoculation (dpi) revealed activation of macrophages in both chicken lines. A strong immune response was induced in cecal tonsils of the susceptible line at 5 dpi. The highest transcriptional activities were observed in spleen tissues of the resistant line at 3 dpi. No increase in the population of CD3⁺ T cells was observed in duodenum of vaccinated birds at 5 dpi indicating a lack of involvement of the adaptive immune system in the transcriptional profiling of the tested genes. There was, however, an increase in the number of macrophages in the duodenum of vaccinated birds. The CVI988/Rispens antigen was detected in the duodenum and cecal tonsils of the susceptible line at 5 dpi but not in the resistant line. This study sheds light on the role of macrophages in vaccine-mediated protection against MD and on the possible development of new recombinant vaccines with enhanced innate immune system activation properties.
Keywords: CVI988/Rispens; Marek’s disease; cecal tonsils; duodenum; macrophages.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Bacon LD, Hunt HD, Cheng HH. A review of the development of chicken lines to resolve genes determining resistance to diseases. Poult Sci. 2000;79:1082–1093. - PubMed
-
- Baigent S, Davison T. Marek's disease virus: biology and life cycle. In: Davison F, Nair V, editors. Marek's Disease: An Evolving Problem. Oxford: Elsevier Academic Press; 2004. pp. 62–77.
-
- Biron CA. Initial and innate responses to viral infections-pattern setting in immunity or disease. Curr Opin Microbiol. 1999;2:374–381. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

