Re(CO)3([18F]FEDA), a novel 18F PET renal tracer: Radiosynthesis and preclinical evaluation
- PMID: 29367095
- PMCID: PMC5817033
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2017.12.001
Re(CO)3([18F]FEDA), a novel 18F PET renal tracer: Radiosynthesis and preclinical evaluation
Abstract
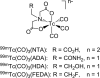
Introduction: Our previous work demonstrated that the 99mTc renal tracer, 99mTc(CO)3(FEDA) (99mTc-1), has a rapid clearance comparable in rats to that of 131I-OIH, the radioactive gold standard for the measurement of effective renal plasma flow. The uncharged fluoroethyl pendant group of 99mTc-1 provides a route to the synthesis of a structurally analogous rhenium-tricarbonyl 18F renal imaging agent, Re(CO)3([18F]FEDA) (18F-1). Our goal was to develop an efficient one-step method for the preparation of 18F-1 and to compare its pharmacokinetic properties with those of 131I-OIH in rats.
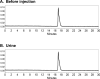
Methods: 18F-1 was prepared by the nucleophilic 18F-fluorination of its tosyl precursor. The labeled compound was isolated by HPLC and subsequently evaluated in Sprague-Dawley rats using 131I-OIH as an internal control and by dynamic PET/CT imaging. Plasma protein binding (PPB) and erythrocyte uptake (RCB) were determined and the urine was analyzed for metabolites.
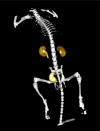
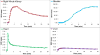
Results: 18F-1 was efficiently prepared as a single species with high radiochemical purity (>99%) and it displayed high radiochemical stability in vitro and in vivo. PPB was 87% and RCB was 21%. Biodistribution studies confirmed rapid renal extraction and high specificity for renal excretion, comparable to that of 131I-OIH, with minimal hepatic/gastrointestinal elimination. The activity in the urine, as a percentage of 131I-OIH, was 92% and 95% at 10 and 60 min, respectively. All other organs (heart, spleen, lungs) showed a negligible tracer uptake (<0.4% ID). Dynamic microPET/CT imaging demonstrated rapid transit of 18F-1 through the kidneys and into the bladder; there was no demonstrable activity in bone verifying the absence of free [18F]fluoride.
Conclusions: 18F-1 exhibited a high specificity for the kidney, rapid renal excretion comparable to that of 131I-OIH and high in vivo radiochemical stability. Not only is 18F-1 a promising PET renal tracer, but it provides a route to the development of a pair of analogous 18F/99mTc renal imaging agents with almost identical structures and comparable pharmacokinetic properties. These promising in vivo results warrant subsequent evaluation in humans.
Keywords: Biodistribution; PET imaging; Radiolabeling; Re(CO)(3)([(18)F]FEDA); Renal radiotracer.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




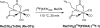
Similar articles
-
The next era of renal radionuclide imaging: novel PET radiotracers.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019 Aug;46(9):1773-1786. doi: 10.1007/s00259-019-04359-8. Epub 2019 May 30. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019. PMID: 31144061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monoanionic 99mTc-tricarbonyl-aminopolycarboxylate complexes with uncharged pendant groups: Radiosynthesis and evaluation as potential renal tubular tracers.Nucl Med Biol. 2017 Apr;47:48-55. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2016.12.008. Epub 2016 Dec 27. Nucl Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28110124 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical evaluation of 99mTc(CO)3-aspartic-N-monoacetic acid, a renal radiotracer with pharmacokinetic properties comparable to 131I-o-iodohippurate.J Nucl Med. 2012 Aug;53(8):1277-83. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.111.102236. Epub 2012 Jun 20. J Nucl Med. 2012. PMID: 22717977 Free PMC article.
-
Al18F-NODA-butyric acid: biological evaluation of a new PET renal radiotracer.Nucl Med Biol. 2014 Mar;41(3):248-53. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2013.12.010. Epub 2013 Dec 26. Nucl Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 24533986 Free PMC article.
-
m-Cyano-p-[18F]fluorohippurate.2012 Oct 24 [updated 2012 Nov 21]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2012 Oct 24 [updated 2012 Nov 21]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 23193621 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
The next era of renal radionuclide imaging: novel PET radiotracers.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019 Aug;46(9):1773-1786. doi: 10.1007/s00259-019-04359-8. Epub 2019 May 30. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019. PMID: 31144061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
11C-PABA as a PET Radiotracer for Functional Renal Imaging: Preclinical and First-in-Human Study.J Nucl Med. 2020 Nov;61(11):1665-1671. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.119.239806. Epub 2020 Mar 20. J Nucl Med. 2020. PMID: 32198314 Free PMC article.
-
Current and future perspectives on functional molecular imaging in nephro-urology: theranostics on the horizon.Theranostics. 2021 Apr 7;11(12):6105-6119. doi: 10.7150/thno.58682. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33897902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Imaging of the Glomerulus via Mesangial Cell Uptake of Radiolabeled Tilmanocept.J Nucl Med. 2019 Sep;60(9):1325-1332. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.118.223727. Epub 2019 Feb 22. J Nucl Med. 2019. PMID: 30796169 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lane BR, Poggio ED, Herts BR, Novick AC, Campbell SC. Renal function assesment in the era of chronic kidney disease: renewed emphasis on renal function centered patient care. J Urol. 2009;182:435–44. - PubMed
-
- Prigent A. Monitoring renal function and limitations of renal function tests. Semin Nucl Med. 2008;38:32–46. - PubMed
-
- Blaufox MD, Aurell M, Bubeck B, Fommei E, Piepsz A, Russell C, et al. Report of the radionuclides in nephrourology committee on renal clearance. J Nucl Med. 1996;37:1883–90. - PubMed
-
- Shikano N, Kanai Y, Kawai K, Ishikawa N, Endou H. Transport of 99mTc-MAG3 via rat renal organic anion transporter 1. J Nucl Med. 2004;45:80–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

