Human Papillomavirus 16 E7 Stabilizes APOBEC3A Protein by Inhibiting Cullin 2-Dependent Protein Degradation
- PMID: 29367246
- PMCID: PMC5972886
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01318-17
Human Papillomavirus 16 E7 Stabilizes APOBEC3A Protein by Inhibiting Cullin 2-Dependent Protein Degradation
Abstract
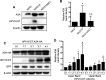
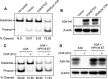
APOBEC3 (A3) mutation signatures have been observed in a variety of human cancer genomes, including those of cervical and head and neck cancers caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. However, the driving forces that promote off-target A3 activity remain mostly unclear. Here, we report a mechanism for the dramatic increase of A3A protein levels in HPV-positive keratinocytes. We show that expression of the viral protein E7 from high-risk HPVs, but not E7 from low-risk HPVs, significantly prolongs the cellular half-life of A3A protein in human keratinocytes and HPV-positive cancer cell lines. We have mapped several residues within the cullin 2 (CUL2) binding motif of HPV16 E7 as being important for mediating A3A protein stabilization. Furthermore, we provide direct evidence that both A3A and HPV16 E7 interact with CUL2, suggesting that the E7-CUL2 complex formed during HPV infection may regulate A3A protein levels in the cell. Using an in vitro cytidine deaminase assay, we show that E7-stabilized A3A remains catalytically active. Taken together, our findings suggest that the HPV oncoprotein E7 dysregulates endogenous A3A protein levels and thus provides novel mechanistic insight into cellular triggers of A3 mutations in HPV-positive cancers.IMPORTANCE Human papillomavirus (HPV) is causally associated with over 5% of all human malignancies. Several recent studies have shown that a subset of cancers, including HPV-positive head and neck and cervical cancers, have distinct mutational signatures potentially caused by members of the APOBEC3 cytidine deaminase family. However, the mechanism that induces APOBEC3 activity in cancer cells is poorly understood. Here, we report that the HPV oncoprotein E7 stabilizes the APOBEC3A (A3A) protein in human keratinocytes by inhibiting ubiquitin-dependent protein degradation in a cullin-dependent manner. Interestingly, the HPV E7-stabilized A3A protein maintains its deaminase activity. These findings provide a new insight into cancer mutagenesis enhanced by virus-induced A3A protein stabilization.
Keywords: APOBEC3; cancer mutagenesis; cervical cancer; cullin; head and neck cancer; innate immunity; papillomavirus; somatic mutation.
Copyright © 2018 Westrich et al.
Figures







References
-
- Jabbar SF, Park S, Schweizer J, Berard-Bergery M, Pitot HC, Lee D, Lambert PF. 2012. Cervical cancers require the continuous expression of the human papillomavirus type 16 E7 oncoprotein even in the presence of the viral E6 oncoprotein. Cancer Res 72:4008–4016. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3085. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

