Evaluation of Two DNA Extraction Methods for Detection of Strongyloides stercoralis Infection
- PMID: 29367294
- PMCID: PMC5869848
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01941-17
Evaluation of Two DNA Extraction Methods for Detection of Strongyloides stercoralis Infection
Abstract
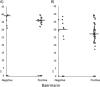
Strongyloides stercoralis is present worldwide, but its prevalence is still uncertain, mainly due to the lack of sensitivity of diagnostic methods. Molecular techniques are under development, but a standardized protocol is still unavailable. We compared the sensitivity of real-time PCR, using two extraction protocols, with that of the Baermann technique. Samples were collected in the framework of the baseline screening of a randomized clinical trial evaluating moxidectin against S. stercoralis in Lao People's Democratic Republic. Two stool samples from each participant were processed by the Baermann method, and one subsample was processed by PCR. DNA was extracted using the QIAamp DNA stool minikit based on the standard protocol for the QIAamp DNA minikit (QIA) and using a modification of the QIA procedure (POL). Subsequently, all extracted samples were analyzed by real-time PCR. Overall, 95 samples were analyzed by the three diagnostic methods. Sixty-nine (72.6%) samples were positive according to the Baermann method, 25 (26.3%) by the QIA method, and 62 (65.3%) by the POL method. The sensitivities were 86% (95% confidence interval [CI], 76.7 to 92.9), 31.0% (95% CI, 21.3 to 42.6), and 78.0% (95% CI, 66.8 to 86.1) for the Baermann, QIA, and POL methods, respectively. The sensitivities calculated for each day of the Baermann method separately were 60% (48.4 to 70.8%) and 64% (52.2 to 74.2%) for days 1 and 2, respectively. In conclusion, the POL method revealed a good performance and was comparable to the Baermann test performed on two stool samples and superior to the Baermann method performed on one stool sample. Additional studies are needed to standardize a PCR protocol for S. stercoralis diagnosis.
Keywords: PCR; Strongyloides stercoralis; diagnosis.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
References
-
- Buonfrate D, Mena MA, Angheben A, Requena-Mendez A, Muñoz J, Gobbi F, Albonico M, Gotuzzo E, Bisoffi Z, COHEMI Project Study Group . 2015. Prevalence of strongyloidiasis in Latin America: a systematic review of the literature. Epidemiol Infect 143:452–460. doi: 10.1017/S0950268814001563. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

