Systematic Functional Characterization of Human 21st Chromosome Orthologs in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 29367452
- PMCID: PMC5844316
- DOI: 10.1534/g3.118.200019
Systematic Functional Characterization of Human 21st Chromosome Orthologs in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
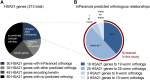
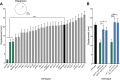
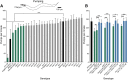
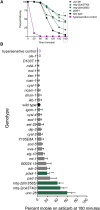
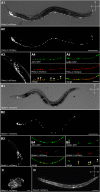
Individuals with Down syndrome have neurological and muscle impairments due to an additional copy of the human 21st chromosome (HSA21). Only a few of ∼200 HSA21 genes encoding proteins have been linked to specific Down syndrome phenotypes, while the remainder are understudied. To identify poorly characterized HSA21 genes required for nervous system function, we studied behavioral phenotypes caused by loss-of-function mutations in conserved HSA21 orthologs in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans We identified 10 HSA21 orthologs that are required for neuromuscular behaviors: cle-1 (COL18A1), cysl-2 (CBS), dnsn-1 (DONSON), eva-1 (EVA1C), mtq-2 (N6ATM1), ncam-1 (NCAM2), pad-2 (POFUT2), pdxk-1 (PDXK), rnt-1 (RUNX1), and unc-26 (SYNJ1). We also found that three of these genes are required for normal release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. This includes a known synaptic gene unc-26 (SYNJ1), as well as uncharacterized genes pdxk-1 (PDXK) and mtq-2 (N6ATM1). As the first systematic functional analysis of HSA21 orthologs, this study may serve as a platform to understand genes that underlie phenotypes associated with Down syndrome.
Keywords: Down syndrome; neurological; neuromuscular; synaptic.
Copyright © 2018 Nordquist et al.
Figures


References
-
- Ahn K.-J., Jeong H. K., Choi H.-S., Ryoo S.-R., Kim Y. J., et al. , 2006. DYRK1A BAC transgenic mice show altered synaptic plasticity with learning and memory defects. Neurobiol. Dis. 22: 463–472. - PubMed
-
- Albertson D. G., Thomson J. N., 1976. The pharynx of Caenorhabditis elegans. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 275: 299–325. - PubMed
-
- Altafaj X., Dierssen M., Baamonde C., Martí E., Visa J., et al. , 2001. Neurodevelopmental delay, motor abnormalities and cognitive deficits in transgenic mice overexpressing Dyrk1A (minibrain), a murine model of Down’s syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 10: 1915–1923. - PubMed
-
- Antonarakis S. E., 2016. Down syndrome and the complexity of genome dosage imbalance. Nat. Rev. Genet. 18: 147–163. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
