Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship Model for HCVNS5B inhibitors based on an Antlion Optimizer-Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System
- PMID: 29367667
- PMCID: PMC5784174
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-19122-y
Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship Model for HCVNS5B inhibitors based on an Antlion Optimizer-Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System
Abstract
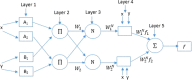
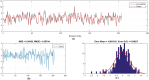
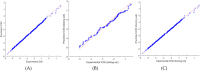
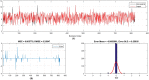
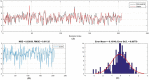
The global prevalence of hepatitis C Virus (HCV) is approximately 3% and one-fifth of all HCV carriers live in the Middle East, where Egypt has the highest global incidence of HCV infection. Quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) models were used in many applications for predicting the potential effects of chemicals on human health and environment. The adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) is one of the most popular regression methods for building a nonlinear QSAR model. However, the quality of ANFIS is influenced by the size of the descriptors, so descriptor selection methods have been proposed, although these methods are affected by slow convergence and high time complexity. To avoid these limitations, the antlion optimizer was used to select relevant descriptors, before constructing a nonlinear QSAR model based on the PIC50 and these descriptors using ANFIS. In our experiments, 1029 compounds were used, which comprised 579 HCVNS5B inhibitors (PIC50 < ~14) and 450 non-HCVNS5B inhibitors (PIC50 > ~14). The experimental results showed that the proposed QSAR model obtained acceptable accuracy according to different measures, where [Formula: see text] was 0.952 and 0.923 for the training and testing sets, respectively, using cross-validation, while [Formula: see text] was 0.8822 using leave-one-out (LOO).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Fallahian F, Najafi A. Epidemiology of hepatitis C in the Middle East. Saudi Journal of Kidney Diseases and Transplantation. 2011;22:31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

