Somatic APC mosaicism and oligogenic inheritance in genetically unsolved colorectal adenomatous polyposis patients
- PMID: 29367705
- PMCID: PMC5839046
- DOI: 10.1038/s41431-017-0086-y
Somatic APC mosaicism and oligogenic inheritance in genetically unsolved colorectal adenomatous polyposis patients
Abstract
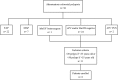
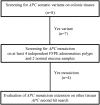
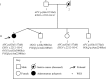
Germline variants in the APC gene cause familial adenomatous polyposis. Inherited variants in MutYH, POLE, POLD1, NTHL1, and MSH3 genes and somatic APC mosaicism have been reported as alternative causes of polyposis. However, ~30-50% of cases of polyposis remain genetically unsolved. Thus, the aim of this study was to investigate the genetic causes of unexplained adenomatous polyposis. Eight sporadic cases with >20 adenomatous polyps by 35 years of age or >50 adenomatous polyps by 55 years of age, and no causative germline variants in APC and/or MutYH, were enrolled from a cohort of 56 subjects with adenomatous colorectal polyposis. APC gene mosaicism was investigated on DNA from colonic adenomas by Sanger sequencing or Whole Exome Sequencing (WES). Mosaicism extension to other tissues (peripheral blood, saliva, hair follicles) was evaluated using Sanger sequencing and/or digital PCR. APC second hit was investigated in adenomas from mosaic patients. WES was performed on DNA from peripheral blood to identify additional polyposis candidate variants. We identified APC mosaicism in 50% of patients. In three cases mosaicism was restricted to the colon, while in one it also extended to the duodenum and saliva. One patient without APC mosaicism, carrying an APC in-frame deletion of uncertain significance, was found to harbor rare germline variants in OGG1, POLQ, and EXO1 genes. In conclusion, our restrictive selection criteria improved the detection of mosaic APC patients. In addition, we showed for the first time that an oligogenic inheritance of rare variants might have a cooperative role in sporadic colorectal polyposis onset.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

