Hypoxia induces miR-153 through the IRE1α-XBP1 pathway to fine tune the HIF1α/VEGFA axis in breast cancer angiogenesis
- PMID: 29367761
- PMCID: PMC5895606
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-017-0089-8
Hypoxia induces miR-153 through the IRE1α-XBP1 pathway to fine tune the HIF1α/VEGFA axis in breast cancer angiogenesis
Abstract
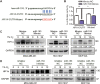
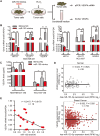
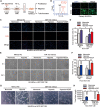
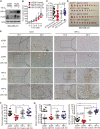
It is well documented that hypoxia activates the hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF1α)/vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) axis to promote angiogenesis in breast cancer. However, it is unclear how this axis is negatively regulated. In this study, we demonstrated that miR-153 directly inhibits expression of HIF1α by binding to the 3'UTR of HIF1A mRNA, as well as suppresses tube formation of primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and breast cancer angiogenesis by decreasing the secretion of VEGFA. Importantly, expression of miR-153 was induced by hypoxia-stimulated ER stress, which activates IRE1α and its downstream transcription factor X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1). X-box binding protein 1 directly binds to the promoter of the miR-153 host gene PTPRN and activates transcription. These results indicate that hypoxia induces miR-153 to fine tune the HIF1α/VEGFA axis in breast cancer angiogenesis and miR-153 could be used for breast cancer anti-angiogenesis therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MiR-5586-5p Suppresses Hypoxia-induced Angiogenesis Through Multiple Targeting of HIF-1α, HBEGF and ADAM17 in Breast Cancer.Anticancer Res. 2025 Feb;45(2):473-489. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.17437. Anticancer Res. 2025. PMID: 39890164
-
The mineral dust-induced gene, mdig, regulates angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in lung adenocarcinoma by modulating the expression of VEGF-A/C/D via EGFR and HIF-1α signaling.Oncol Rep. 2021 May;45(5):60. doi: 10.3892/or.2021.8011. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Oncol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33760153
-
MicroRNA-503 targets FGF2 and VEGFA and inhibits tumor angiogenesis and growth.Cancer Lett. 2013 Jun 10;333(2):159-69. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.01.028. Epub 2013 Jan 22. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 23352645
-
Roles of Post-Translational Modifications of Transcription Factors Involved in Breast Cancer Hypoxia.Molecules. 2025 Feb 1;30(3):645. doi: 10.3390/molecules30030645. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 39942749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of vascular endothelial growth factor a polymorphisms in breast cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2012 Nov 13;13(11):14845-64. doi: 10.3390/ijms131114845. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23203097 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A vicious circle in breast cancer: The interplay between inflammation, reactive oxygen species, and microRNAs.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 26;12:980694. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.980694. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36226048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles of endoplasmic reticulum stress in the cellular plasticity of cancer cells.Front Oncol. 2023 Feb 20;13:1110881. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1110881. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36890838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-153 impairs presynaptic plasticity by blocking vesicle release following chronic brain hypoperfusion.Cell Commun Signal. 2020 Apr 6;18(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12964-020-00551-8. Cell Commun Signal. 2020. PMID: 32252776 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of PTPRN Promotes Metastasis of Lung Adenocarcinoma and Suppresses NK Cell Cytotoxicity.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 2;9:622018. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.622018. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34150744 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the role of exosomal MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers in preeclampsia.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 19;15:1385950. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1385950. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38566996 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Folkman J. How is blood vessel growth regulated in normal and neoplastic tissue? G.H.A. Clowes memorial Award lecture. Cancer Res. 1986;46:467–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

