A system view and analysis of essential hypertension
- PMID: 29369145
- PMCID: PMC6927246
- DOI: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001680
A system view and analysis of essential hypertension
Abstract
Objectives: The goal of this study was to investigate genes associated with essential hypertension from a system perspective, making use of bioinformatic tools to gain insights that are not evident when focusing at a detail-based resolution.
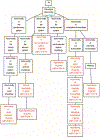
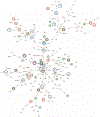
Methods: Using various databases (pathways, Genome Wide Association Studies, knockouts etc.), we compiled a set of about 200 genes that play a major role in hypertension and identified the interactions between them. This enabled us to create a protein-protein interaction network graph, from which we identified key elements, based on graph centrality analysis. Enriched gene regulatory elements (transcription factors and microRNAs) were extracted by motif finding techniques and knowledge-based tools.
Results: We found that the network is composed of modules associated with functions such as water retention, endothelial vasoconstriction, sympathetic activity and others. We identified the transcription factor SP1 and the two microRNAs miR27 (a and b) and miR548c-3p that seem to play a major role in regulating the network as they exert their control over several modules and are not restricted to specific functions. We also noticed that genes involved in metabolic diseases (e.g. insulin) are central to the network.
Conclusion: We view the blood-pressure regulation mechanism as a system-of-systems, composed of several contributing subsystems and pathways rather than a single module. The system is regulated by distributed elements. Understanding this mode of action can lead to a more precise treatment and drug target discovery. Our analysis suggests that insulin plays a primary role in hypertension, highlighting the tight link between essential hypertension and diseases associated with the metabolic syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of rifampin-regulated functional modules and related microRNAs in human hepatocytes based on the protein interaction network.BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 22;17 Suppl 7(Suppl 7):517. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2909-6. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27557147 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms underlying gliomas and glioblastoma pathogenesis revealed by bioinformatics analysis of microarray data.Med Oncol. 2017 Sep 26;34(11):182. doi: 10.1007/s12032-017-1043-x. Med Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28952134
-
Systems biology approach identifies key regulators and the interplay between miRNAs and transcription factors for pathological cardiac hypertrophy.Gene. 2019 May 25;698:157-169. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.02.056. Epub 2019 Mar 5. Gene. 2019. PMID: 30844478
-
MicroRNA mediated network motifs in autoimmune diseases and its crosstalk between genes, functions and pathways.J Immunol Methods. 2017 Jan;440:19-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2016.10.002. Epub 2016 Oct 8. J Immunol Methods. 2017. PMID: 27729225
-
microRNAs in Essential Hypertension and Blood Pressure Regulation.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;888:215-35. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22671-2_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26663185 Review.
Cited by
-
Identifying susceptibility genes for essential hypertension by transcriptome-wide association study.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022 Nov 21;32:101387. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2022.101387. eCollection 2022 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022. PMID: 36438602 Free PMC article.
-
Network medicine: an approach to complex kidney disease phenotypes.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2023 Jul;19(7):463-475. doi: 10.1038/s41581-023-00705-0. Epub 2023 Apr 11. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37041415 Review.
-
Blood Pressure Regulation Evolved from Basic Homeostatic Components.Biomedicines. 2021 Apr 25;9(5):469. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9050469. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33923023 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding RNAs in the Regulatory Network of Hypertension.Hypertension. 2018 Nov;72(5):1047-1059. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.11126. Hypertension. 2018. PMID: 30354825 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Protein-protein interaction network-based integration of GWAS and functional data for blood pressure regulation analysis.Hum Genomics. 2024 Feb 8;18(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s40246-023-00565-6. Hum Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38326862 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Garcia EA, Newhouse S, Caulfield MJ, Munroe PB. Genes and hypertension. Curr Pharm Des 2003; 9:1679–1689. - PubMed
-
- Cowley AW Jr. The genetic dissection of essential hypertension. Nat Rev Genet 2006; 7:829–840. - PubMed
-
- Padmanabhan S, Caulfield M, Dominiczak AF. Genetic and molecular aspects of hypertension. Circ Res 2015; 116:937–959. - PubMed
-
- Coffman TM. Under pressure: the search for the essential mechanisms of hypertension. Nat Med 2011; 17:1402–1409. - PubMed
-
- Zheng J Rao DC, Shi G. An update on genome-wide association studies of hypertension. Appl Inform 2015; 2:10.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

