Recent Advances in Nanoporous Membranes for Water Purification
- PMID: 29370128
- PMCID: PMC5853697
- DOI: 10.3390/nano8020065
Recent Advances in Nanoporous Membranes for Water Purification
Abstract
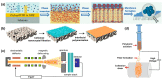
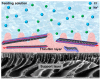
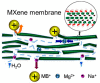
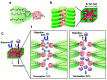
Nanoporous materials exhibit wide applications in the fields of electrocatalysis, nanodevice fabrication, energy, and environmental science, as well as analytical science. In this review, we present a summary of recent studies on nanoporous membranes for water purification application. The types and fabrication strategies of various nanoporous membranes are first introduced, and then the fabricated nanoporous membranes for removing various water pollutants, such as salt, metallic ions, anions, nanoparticles, organic chemicals, and biological substrates, are demonstrated and discussed. This work will be valuable for readers to understand the design and fabrication of various nanoporous membranes, and their potential purification mechanisms towards different water pollutants. In addition, it will be helpful for developing new nanoporous materials for quick, economic, and high-performance water purification.
Keywords: fabrication; graphene; nanoporous membrane; purification mechanism; two-dimensional materials; water pollutants; water purification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


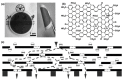
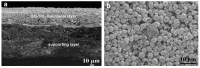

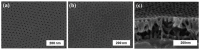
References
-
- Schaider L.A., Rudel R.A., Ackerman J.M., Dunagan S.C., Brody J.G. Pharmaceuticals, perfluorosurfactants, and other organic wastewater compounds in public drinking water wells in a shallow sand and gravel aquifer. Sci. Total Environ. 2014;468:384–393. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.067. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Daniel S., Limson J.L., Dairam A., Watkins G.M., Daya S. Through metal binding, curcumin protects against lead- and cadmium-induced lipid peroxidation in rat brain homogenates and against lead-induced tissue damage in rat brain. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2004;98:266–275. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2003.10.014. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

