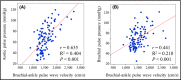
Relationship between brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity and invasively measured aortic pulse pressure
- PMID: 29370481
- PMCID: PMC8030939
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.13200
Relationship between brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity and invasively measured aortic pulse pressure
Abstract
Although brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV) has been widely used as an index of arterial stiffness, no consensus exists about whether baPWV can reflect central aortic stiffness. The authors investigated the association between baPWV and invasively measured aortic pulse pressure (APP) in a total of 109 consecutive patients (mean age, 62.3 ± 11.3 years; 67.9% men). Most patients (91%) had obstructive coronary artery disease, and mean baPWV and APP values were 1535 ± 303 cm/s and 66.8 ± 22.5 mm Hg, respectively. In univariate analysis, there was a significant linear correlation between baPWV and APP (r = .635, P < .001). The correlation between baPWV and APP remained significant even after controlling for potential confounders (β = 0.574, P < .001; R2 = .469). Arterial stiffness measured by baPWV showed a strong positive correlation with invasively measured APP, independent of clinical confounders. Therefore, baPWV can be a good marker of central aortic stiffness.
Keywords: aortic pulse pressure; aortic stiffness; correlation; pulse wave velocity.
©2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Comment in
-
Peripheral arterial stiffness as a surrogate of central hemodynamics: A new era for cardiovascular risk estimation?J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2018 Mar;20(3):469-471. doi: 10.1111/jch.13204. Epub 2018 Jan 25. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2018. PMID: 29370478 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Dart AM, Kingwell BA. Pulse pressure––a review of mechanisms and clinical relevance. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001;37:975‐984. - PubMed
-
- Safar ME, Levy BI, Struijker‐Boudier H. Current perspectives on arterial stiffness and pulse pressure in hypertension and cardiovascular diseases. Circulation. 2003;107:2864‐2869. - PubMed
-
- Vlachopoulos C, Aznaouridis K, Stefanadis C. Prediction of cardiovascular events and all‐cause mortality with arterial stiffness: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55:1318‐1327. - PubMed
-
- Brown DW, Giles WH, Croft JB. Left ventricular hypertrophy as a predictor of coronary heart disease mortality and the effect of hypertension. Am Heart J. 2000;140:848‐856. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical