Home-based physical activity incentive and education program in subacute phase of stroke recovery (Ticaa'dom): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 29370824
- PMCID: PMC5785899
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-017-2410-9
Home-based physical activity incentive and education program in subacute phase of stroke recovery (Ticaa'dom): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Stroke causes functional decline, psychological disorders and cognitive impairments that affect activities of daily living and quality of life. Although physical activity (PA) is beneficial in stroke recovery, PA recommendations are rarely met after hospital discharge. There is presently no standard strategy for monitoring and inciting PA at home during the subacute phase of stroke recovery. The main aim of this study is to evaluate the effects of a home-based physical activity incentive and education program (Ticaa'dom) on functional capacity in subacute stroke patients.
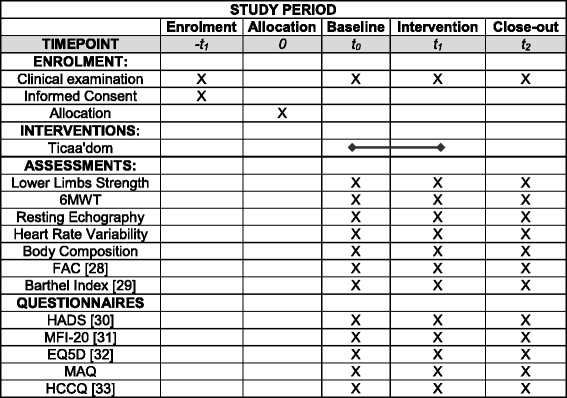
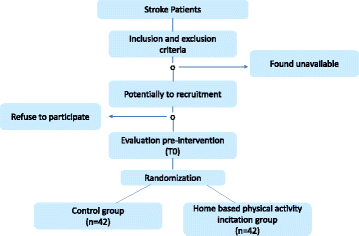
Methods: This study is a comparative prospective, observer-blinded, monocentric, parallel, randomized controlled clinical trial. This study will include 84 patients: 42 patients in the home-based physical activity incentive group (HB-PAI) and 42 in the control group (CG). The intervention group will follow the HB-PAI program over 6 months: their PA will be monitored with an accelerometer during the day at home while they record their subjective perception of PA on a chart; they will observe a weekly telephone call and a home visit every three weeks. The CG will receive traditional medical care over 12 months. The main study outcome will be the distance on a 6-minute walk test. Secondary outcomes will include measurements of lower limb strength, independence level, body composition, cardiac analysis, fatigue and depression state.
Discussion: The results of this trial will demonstrate the value of implementing the Ticaa'dom program during the subacute phase of stroke recovery.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT01822938 . Registered on 25 March 2013.
Keywords: Home-based exercise; Physical activity; RCT; Rehabilitation; Secondary prevention; Stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the French IPC. The Committee reference number is 2012-A01456-37. The investigators will obtain written informed consent from all participants in the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


References
-
- Krishnamurthi RV, Feigin VL, Forouzanfar MH, Mensah GA, Connor M, Bennett DA, et al. Global and regional burden of first-ever ischaemic and haemorrhagic stroke during 1990–2010: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet Glob Health. 2013;1:e259–81. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(13)70089-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

