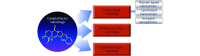
Camptothecin-based nanodrug delivery systems
- PMID: 29372102
- PMCID: PMC5785165
- DOI: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2017.0099
Camptothecin-based nanodrug delivery systems
Abstract
The drug camptothecin has a wide range of antitumor effects in cancers including gastric cancer, rectal and colon cancer, liver cancer, and lung cancer. Camptothecin-based drugs inhibit topoisomerase 1 (Topo 1), leading to destruction of DNA, and are currently being used as important chemotherapeutic agents in clinical antitumor treatment. However, the main obstacle associated with cancer therapy is represented by systemic toxicity of conventional anticancer drugs and their low accumulation at the tumor site. In addition, low bioavailability, poor water solubility, and other shortcomings hinder their anticancer activity. Different from traditional pharmaceutical preparations, nanotechnology-dependent nanopharmaceutical preparations have become one of the main strategies for different countries worldwide to overcome drug development problems. In this review, we summarized the current hotspots and discussed a variety of camptothecin-based nanodrugs for cancer therapy. We hope that through this review, more efficient drug delivery systems could be designed with potential applications in clinical cancer therapy.
Keywords: Camptothecins; cancer therapy; drug delivery system; nanomedicine.
Figures
References
-
- Wall ME, Wani MC, Cook CE, Palmer KH, McPhail AT, Sim GA. Plant antitumor agents. I. The isolation and structure of camptothecin, a novel alkaloidal leukemia and tumor inhibitor from Camptotheca acuminata . J Am Chem Soc. 1966;88:3888–90.
-
- Hsiang YH, Hertzberg R, Hecht S, Liu LF. Camptothecin induces protein-linked DNA breaks via mammalian DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:14873–8. - PubMed
-
- Wall ME. Camptothecin and taxol: discovery to clinic. Med Res Rev. 1998;18:299–314. - PubMed
-
- O’Leary J, Muggia FM. Camptothecins: a review of their development and schedules of administration. Eur J Cancer. 1998;34:1500–8. - PubMed
-
- Potmesil M. Camptothecins: from bench research to hospital wards. Cancer Res. 1994;54:1431–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources