The Effect of Topical Substance-P Plus Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1) on Epithelial Healing After Photorefractive Keratectomy in Rabbits
- PMID: 29372114
- PMCID: PMC5782824
- DOI: 10.1167/tvst.7.1.12
The Effect of Topical Substance-P Plus Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1) on Epithelial Healing After Photorefractive Keratectomy in Rabbits
Abstract
Purpose: To determine whether topical Substance-P (SP) plus insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) can improve corneal healing after photorefractive surface ablation in a rabbit.
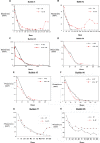
Methods: After a 9.0-mm corneal de-epithelialization using a combination of chemical (18% alcohol) and mechanical debridement, excimer photorefractive surface ablation was performed bilaterally in eight rabbits (16 eyes) with an 8.0-mm ablation zone and 70-μm depth. The right eye was treated with SP (250 μg/mL) and IGF-1 (25 ng/mL) in hyaluronic acid, one drop twice a day, and the other eye treated with only hyaluronic acid. The epithelial healing process was documented photographically twice a day until healing was complete. Six rabbits were sacrificed 6 weeks after photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) and corneas examined histologically.
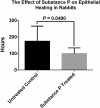
Results: Seven of eight rabbit eyes treated with SP/IGF-1 healed in a shorter time than the untreated eye. For rabbit #6, both eyes healed at the same time. The average healing time (total time until wound closure) for the treated eyes was 99 hours, while the average healing time for the untreated eyes was 170 hours (P = 0.0490). A persistent epithelial defect was found in two of the nontreated eyes but none in the treated eyes. Corneal pathology showed some degree of epithelial separation in the central corneal wound in three out of six nontreated eyes and in just the treated eye of rabbit #6.
Conclusion: Topical SP plus IGF-1 increases the epithelial healing rate after PRK. There may have been beneficial effects upon cell adhesion as well.
Translational relevance: Better and faster healing.
Keywords: IGF-1; Substance P; photorefractive keratectomy; wound healing.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of topical fluoroquinolones on corneal re-epithelialization after excimer laser keratectomy.J Cataract Refract Surg. 1997 Jul-Aug;23(6):845-8. doi: 10.1016/s0886-3350(97)80241-6. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1997. PMID: 9292666
-
Comparison of corneal epithelial wound healing after photorefractive and lamellar keratectomy.J Refract Surg. 1996 Mar-Apr;12(3):352-7. doi: 10.3928/1081-597X-19960301-09. J Refract Surg. 1996. PMID: 8705710
-
Epithelial healing rates with topical ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, and ofloxacin with artificial tears after photorefractive keratectomy.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000 May;26(5):690-4. doi: 10.1016/s0886-3350(00)00411-9. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000. PMID: 10831898 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of 50% ethanol and mechanical epithelial debridement on corneal structure before and after excimer photorefractive keratectomy.Cornea. 1997 Sep;16(5):571-9. Cornea. 1997. PMID: 9294692
-
[Neurotrophic keratopathy--studies on substance P and the clinical significance of corneal sensation].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 1997 Dec;101(12):948-74. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 1997. PMID: 9436358 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
The use of fat grafting and platelet-rich plasma for wound healing: A review of the current evidence.Int Wound J. 2019 Feb;16(1):275-285. doi: 10.1111/iwj.13029. Epub 2018 Nov 20. Int Wound J. 2019. PMID: 30460739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploratory Phase II Multicenter, Open-Label, Clinical Trial of ST266, a Novel Secretome for Treatment of Persistent Corneal Epithelial Defects.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2022 Jan 3;11(1):8. doi: 10.1167/tvst.11.1.8. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 34994777 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Insulin eye drops improve corneal wound healing in STZ-induced diabetic mice by regulating corneal inflammation and neuropeptide release.BMC Ophthalmol. 2024 Apr 9;24(1):155. doi: 10.1186/s12886-024-03436-3. BMC Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38594682 Free PMC article.
-
The Regenerative Potential of Substance P.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 11;23(2):750. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020750. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35054936 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The IGF/Insulin-IGFBP Axis in Corneal Development, Wound Healing, and Disease.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Mar 3;11:24. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00024. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 32194500 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hirst LW, Kenyon KR, Fogle JA, Hanninen L, Stark WJ. . Comparative studies of corneal surface injury in the monkey and rabbit. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981; 99: 1066– 1073. - PubMed
-
- Kenyon KR, Berman M, Rose J, Gage J. . Prevention of stromal ulceration in the alkali-burned rabbit cornea by glued-on contact lens. Evidence for the role of polymorphonuclear leukocytes in collagen degradation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1979; 18: 570– 587. - PubMed
-
- Nakayasu K. . Stromal changes following removal of epithelium in rat cornea. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 1988; 32: 113– 125. - PubMed
-
- Dohlman CH. . The function of the corneal epithelium in health and disease. The Jonas S. Friedenwald Memorial Lecture. Invest Ophthalmol. 1971; 10: 383– 407. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

