Skeleton-Controlled pDNA Delivery of Renewable Steroid-Based Cationic Lipids, the Endocytosis Pathway Analysis and Intracellular Localization
- PMID: 29373505
- PMCID: PMC5855591
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19020369
Skeleton-Controlled pDNA Delivery of Renewable Steroid-Based Cationic Lipids, the Endocytosis Pathway Analysis and Intracellular Localization
Abstract
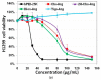
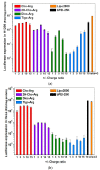
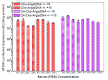
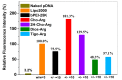
Using renewable and biocompatible natural-based resources to construct functional biomaterials has attracted great attention in recent years. In this work, we successfully prepared a series of steroid-based cationic lipids by integrating various steroid skeletons/hydrophobes with (l-)-arginine headgroups via facile and efficient synthetic approach. The plasmid DNA (pDNA) binding affinity of the steroid-based cationic lipids, average particle sizes, surface potentials, morphologies and stability of the steroid-based cationic lipids/pDNA lipoplexes were disclosed to depend largely on the steroid skeletons. Cellular evaluation results revealed that cytotoxicity and gene transfection efficiency of the steroid-based cationic lipids in H1299 and HeLa cells strongly relied on the steroid hydrophobes. Interestingly, the steroid lipids/pDNA lipoplexes inclined to enter H1299 cells mainly through caveolae and lipid-raft mediated endocytosis pathways, and an intracellular trafficking route of "lipid-raft-mediated endocytosis→lysosome→cell nucleic localization" was accordingly proposed. The study provided possible approach for developing high-performance steroid-based lipid gene carriers, in which the cytotoxicity, gene transfection capability, endocytosis pathways, and intracellular trafficking/localization manners could be tuned/controlled by introducing proper steroid skeletons/hydrophobes. Noteworthy, among the lipids, Cho-Arg showed remarkably high gene transfection efficacy, even under high serum concentration (50% fetal bovine serum), making it an efficient gene transfection agent for practical application.
Keywords: endocytosis pathway; gene delivery; serum-compatible; steroid; structure–function relationships.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
'Click' synthesized sterol-based cationic lipids as gene carriers, and the effect of skeletons and headgroups on gene delivery.Bioorg Med Chem. 2013 Nov 1;21(21):6366-77. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2013.08.047. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Bioorg Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 24063908
-
Achieving high gene delivery performance with caveolae-mediated endocytosis pathway by (l)-arginine/(l)-histidine co-modified cationic gene carriers.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016 Dec 1;148:73-84. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.08.035. Epub 2016 Aug 22. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016. PMID: 27591573
-
Effect of hydrophobic tails of plier-like cationic lipids on nucleic acid delivery and intracellular trafficking.Int J Pharm. 2020 Jan 5;573:118798. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118798. Epub 2019 Nov 20. Int J Pharm. 2020. PMID: 31759106
-
Lipoplex morphologies and their influences on transfection efficiency in gene delivery.J Control Release. 2007 Nov 20;123(3):184-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2007.08.022. Epub 2007 Aug 24. J Control Release. 2007. PMID: 17913276 Review.
-
On the mechanism of cationic amphiphile-mediated transfection. To fuse or not to fuse: is that the question?J Membr Biol. 2002 Oct 1;189(3):167-79. doi: 10.1007/s00232-002-1015-7. J Membr Biol. 2002. PMID: 12395282 Review.
Cited by
-
Microfluidic-Based Cationic Cholesterol Lipid siRNA Delivery Nanosystem: Highly Efficient In Vitro Gene Silencing and the Intracellular Behavior.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 3;23(7):3999. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073999. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409359 Free PMC article.
-
Lipophilic Polyamines as Promising Components of Liposomal Gene Delivery Systems.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jun 21;13(6):920. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13060920. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34205825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural steroid-based cationic copolymers cholesterol/diosgenin-r-PDMAEMAs and their pDNA nanoplexes: impact of steroid structures and hydrophobic/hydrophilic ratios on pDNA delivery.RSC Adv. 2021 Jun 1;11(32):19450-19460. doi: 10.1039/d1ra00223f. eCollection 2021 May 27. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35479247 Free PMC article.
-
Glycopolymer nanomicelles: pH-responsive drug delivery, endocytosis pathway, autophagy behavior, and the effect of autophagy inhibitors.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2025 Jun 6;36(1):47. doi: 10.1007/s10856-024-06837-4. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2025. PMID: 40478478 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albrecht M.A., Evans C.W., Raston C.L. Green chemistry and the health implications of nanoparticles. Green Chem. 2006;8:417–432. doi: 10.1039/b517131h. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

