Epigallocatechin-3-gallate confers protection against corticosterone-induced neuron injuries via restoring extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/protein kinase B signaling pathways
- PMID: 29373584
- PMCID: PMC5786317
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192083
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate confers protection against corticosterone-induced neuron injuries via restoring extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/protein kinase B signaling pathways
Abstract
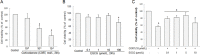
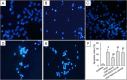
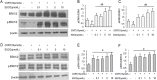
Extensive studies suggested epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) has significant neuroprotection against multiple central neural injuries, but the underlying mechanisms still remain poorly elucidated. Here we provide evidence to support the possible involvement of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) and phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/ protein kinase B (PI3K/AKT) pathways in EGCG-mediated protection against corticosterone-induced neuron injuries. As an essential stress hormone, corticosterone could induce obvious neurotoxicity in primary hippocampal neurons. Pre-treatment with EGCG ameliorated the corticosterone-induced neuronal injuries; however, it was blocked by pharmacological inhibitors for ERK1/2 (U0126) and PI3K/AKT (LY294002). Furthermore, the results confirmed that EGCG restored the corticosterone-induced decrease of ERK1/2 and PI3K/AKT phosphorylation, and attenuated the corticosterone-induced reduction of peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α (PGC-1α) expression and ATP production. Taken together, these findings indicated that EGCG has significant neuroprotection against corticosterone-induced neuron injuries partly via restoring the ERK1/2 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways as well as the PGC-1α-mediated ATP production.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

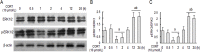



References
-
- Yamamoto N, Shibata M, Ishikuro R, Tanida M, Taniguchi Y, Ikeda-Matsuo Y, et al. Epigallocatechin gallate induces extracellular degradation of amyloid β-protein by increasing neprilysin secretion from astrocytes through activation of ERK and PI3K pathways. Neuroscience. 2017; 362:70–78. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.08.030 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Xicota L, Rodriguez-Morato J, Dierssen M, de la Torre R. Potential Role of (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) in the Secondary Prevention of Alzheimer Disease. Curr Drug Targets. 2017; 18:174–195. doi: 10.2174/1389450116666150825113655 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gu H, Nie Y, Tong Q, Tang Y, Zeng Y, Jing K, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Attenuates Impairment of Learning and Memory in Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress-Treated Rats by Restoring Hippocampal Autophagic Flux. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e112683 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112683 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhao X, Liu F, Jin H, Li R, Wang Y, Zhang W, et al. Involvement of PKCα and ERK1/2 signaling pathways in EGCG's protection against stress-induced neural injuries in Wistar rats. Neuroscience. 2017; 346:226–237. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.01.025 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen WQ, Zhao XL, Wang DL, Li ST, Hou Y, Hong Y, et al. Effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate on behavioral impairments induced by psychological stress in rats. Exp Bio Med. 2010; 235: 577–583. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

