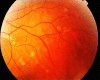
Congenital Hypertrophy of Retinal Pigment Epithelium for Diagnosis of Familial Adenomatous Polyposis - the First FAP registry in Iran
- PMID: 29373909
- PMCID: PMC5844612
- DOI: 10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.1.167
Congenital Hypertrophy of Retinal Pigment Epithelium for Diagnosis of Familial Adenomatous Polyposis - the First FAP registry in Iran
Abstract
Objective: Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), an autosomal dominant inherited disorder is characterized by the presence of multiple adenomatous colorectal polyps, which can develop into cancer during early adulthood. Therefore, early diagnosis is essential. Most FAP patients have several extracolonic manifestations, including congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium (CHRPE). Whereas genetic markers may provide the main route to detection of ‘‘at risk’’ subjects , at present this approach is clearly limited and searches for a noninvasive phenotypic marker continue to be high priority.The aim of this study was to describe the pattern of distribution of CHRPE lesions and evaluate their diagnostic value in FAP patients and their family members in a local population. Methods: A total of 23 FAP patients and 26 relatives belonging to 12 families at high risk of developing FAP were subjected to colonoscopic and ophthalmological examination. Result: Retinal examinations demonstrated prevalences of CHRPE in FAP patents and their siblings of 78% and 38%, respectively. We were able to illustrate a significant correlation between FAP disease and the presence of retinal lesions. Sensitivity and specificity of CHRPE as a screening test to detect the presence of FAP are 78.3% and 61.5%, respectively, with a positive predictive value of 64.3% and a negative predictive value of 76.2 %. A “lesion form” significant difference was found between FAP and normal participants.Spearman nonparametric analysis revealed no correlation between age and number or size of lesions. Conclusion: Multiple CHRPE lesions are a diagnostic feature of FAP patients They are specific and sensitive clinical markers of this disease (specificity 60% and sensitivity 77%).
Keywords: Congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium; familial adenomatous polyposis; Iran.
Creative Commons Attribution License
Figures
References
-
- Anne T, Christine P. Fundus lesions of adenomatous polyposis. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 1999;10:168–72. - PubMed
-
- Chen CS, Phillips KD, Grist S, et al. Congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium (CHRPE) in familial colorectal cancer. Familial Cancer. 2006;5:397–404. - PubMed
-
- Coleman P, Barnard NA. Congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium:prevalence and ocular features in the optometric population. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2007;27:547–55. - PubMed
-
- Cruz-Correa M, Giardiello FM. Familial adenomatous polyposis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003;58:885–94. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous