Ring finger protein 145 (RNF145) is a ubiquitin ligase for sterol-induced degradation of HMG-CoA reductase
- PMID: 29374057
- PMCID: PMC5857978
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001260
Ring finger protein 145 (RNF145) is a ubiquitin ligase for sterol-induced degradation of HMG-CoA reductase
Abstract
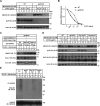
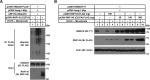
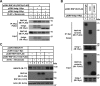
Cholesterol biosynthesis is tightly regulated in the cell. For example, high sterol concentrations can stimulate degradation of the rate-limiting cholesterol biosynthetic enzyme 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (HMG-CoA reductase, HMGCR). HMGCR is broken down by the endoplasmic reticulum membrane-associated protein complexes consisting of insulin-induced genes (Insigs) and the E3 ubiquitin ligase gp78. Here we found that HMGCR degradation is partially blunted in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells lacking gp78 (gp78-KO). To identify other ubiquitin ligase(s) that may function together with gp78 in triggering HMGCR degradation, we performed a small-scale short hairpin RNA-based screening targeting endoplasmic reticulum-localized E3s. We found that knockdown of both ring finger protein 145 (Rnf145) and gp78 genes abrogates sterol-induced degradation of HMGCR in CHO cells. We also observed that RNF145 interacts with Insig-1 and -2 proteins and ubiquitinates HMGCR. Moreover, the tetrapeptide sequence YLYF in the sterol-sensing domain and the Cys-537 residue in the RING finger domain were essential for RNF145 binding to Insigs and RNF145 E3 activity, respectively. Of note, amino acid substitutions in the YLYF or of Cys-537 completely abolished RNF145-mediated HMGCR degradation. In summary, our study reveals that RNF145, along with gp78, promotes HMGCR degradation in response to elevated sterol levels and identifies residues essential for RNF145 function.
Keywords: ER-associated degradation; HMG-CoA reductase; Insig; RNF145; cholesterol metabolism; gp78; lipid; ubiquitin ligase; ubiquitylation (ubiquitination).
© 2018 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures



Similar articles
-
The sterol-responsive RNF145 E3 ubiquitin ligase mediates the degradation of HMG-CoA reductase together with gp78 and Hrd1.Elife. 2018 Dec 13;7:e40009. doi: 10.7554/eLife.40009. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30543180 Free PMC article.
-
Sterol-induced degradation of HMG CoA reductase depends on interplay of two Insigs and two ubiquitin ligases, gp78 and Trc8.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Dec 20;108(51):20503-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1112831108. Epub 2011 Dec 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 22143767 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of HMG-CoA reductase and Insig-1 by enzymes of the ubiquitin-proteasome system.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Dec;23(23):4484-94. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-08-0631. Epub 2012 Oct 19. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 23087214 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-mediated regulation of sterol homeostasis.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2020 Aug;65:103-111. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2020.04.010. Epub 2020 Jun 21. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32580085 Review.
-
Control of cholesterol synthesis through regulated ER-associated degradation of HMG CoA reductase.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2010 Jun;45(3):185-98. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2010.485605. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20482385 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Insulin-induced gene 2 protects against hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury via metabolic remodeling.J Transl Med. 2023 Oct 19;21(1):739. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04564-y. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37858181 Free PMC article.
-
Enzymes in the Cholesterol Synthesis Pathway: Interactomics in the Cancer Context.Biomedicines. 2021 Jul 26;9(8):895. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9080895. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34440098 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of glial size by eicosapentaenoic acid through a novel Golgi apparatus mechanism.PLoS Biol. 2020 Dec 28;18(12):e3001051. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001051. eCollection 2020 Dec. PLoS Biol. 2020. PMID: 33370778 Free PMC article.
-
The ubiquitin E3 ligase BFAR promotes degradation of PNPLA3.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Feb 6;121(6):e2312291121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2312291121. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38294943 Free PMC article.
-
Cholesterol metabolism: physiological regulation and diseases.MedComm (2020). 2024 Feb 24;5(2):e476. doi: 10.1002/mco2.476. eCollection 2024 Feb. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 38405060 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Altmann S. W., Davis H. R. Jr., Zhu L. J., Yao X., Hoos L. M., Tetzloff G., Iyer S. P., Maguire M., Golovko A., Zeng M., Wang L., Murgolo N., and Graziano M. P. (2004) Niemann-Pick C1 Like 1 protein is critical for intestinal cholesterol absorption. Science 303, 1201–1204 10.1126/science.1093131 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

