Dose Calculation Accuracy of AAA and AcurosXB Algorithms for Small Central and Interface Lung Lesions - Verification with Gafchromic Film Dosimetry
- PMID: 29374410
- PMCID: PMC5844627
- DOI: 10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.1.253
Dose Calculation Accuracy of AAA and AcurosXB Algorithms for Small Central and Interface Lung Lesions - Verification with Gafchromic Film Dosimetry
Abstract
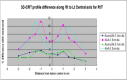
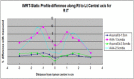
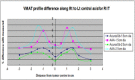
Dose calculation for small field radiotherapy with heterogeneity often involves discrepancies, so that algorithms used by treatment planning systems (TPS) should be evaluated with reference to achieving optimal treatment results. Accuracy of two model based algorithms, AcurosXB (AcXB) and the analytical anisotropic algorithm (AAA) from Eclipse TPS, were here tested. Measurements are made using Gafchromic EBT3 films with indigenously generated lung phantoms irradiated with 6 MV photons. Lung phantoms contained two types of tumor plugs, one kept at an interface attached to the chest wall in right lung (RIT) and the other at the centre of the left lung (LCT). RIT and LCT were studied with two different tumor diameters, 1.5 cm and 2.5 cm. Scanned images were planned in TPS with 3D-CRT, IMRT and VMAT and individual plans for each tumor were irradiated keeping the Gafchromic film at the centre of the tumor to evaluate the dose distribution in the central plane. Both algorithms, irrespective of delivery techniques, showed more deviation with smaller than larger diameter tumors. Also, both demonstrated maximum deviation at the junction of tumor and lung in both RIT and LCT cases. However, the deviation observed was higher with AAA and a minimal acceptable deviation of within 4 % was achieved with AcurosXB.
Keywords: TPS algorithms; lung heterogeneity; dose plane.
Creative Commons Attribution License
Figures






References
-
- Khan FM, Gibbons JP. ‘three dimensional conformal radiation therapy’. Philadelphia, PA: lippincot Williams and Wilkins; 2014. The physics of radiation therapy; pp. 413–29.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

