Epoetin beta pegol for treatment of anemia ameliorates deterioration of erythrocyte quality associated with chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 29374477
- PMCID: PMC5787256
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-018-0818-4
Epoetin beta pegol for treatment of anemia ameliorates deterioration of erythrocyte quality associated with chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Background: Epoetin beta pegol (continuous erythropoietin receptor activator; C.E.R.A.) is currently widely used for the treatment of anemia associated with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Therapeutic control of anemia is assessed by monitoring haemoglobin (Hb) levels. However, certain qualitative aspects of erythrocytes are also impaired in CKD, including loss of deformability and shortened life-span. Therefore, monitoring Hb alone could potentially fail to reveal pathological changes in erythrocytes. Focusing on erythrocyte quality in CKD may lead to more effective anemia therapy with C.E.R.A.
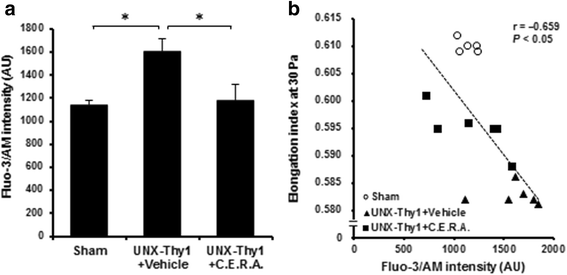
Methods: A CKD rat model was induced by uninephrectomy followed by anti-Thy1.1 antibody injection. From 5 weeks after the operation, C.E.R.A. (0.6 μg/kg) or vehicle was administered every 2 weeks. Erythrocyte deformability was quantified with ektacytometry and erythrocyte turnover was estimated by biotin labeling. Intracellular calcium level was assessed by Fluo-3/AM.
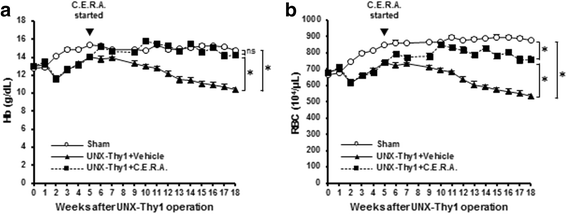
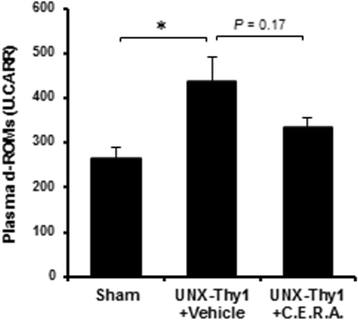
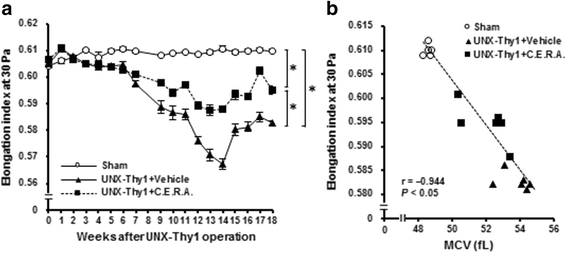
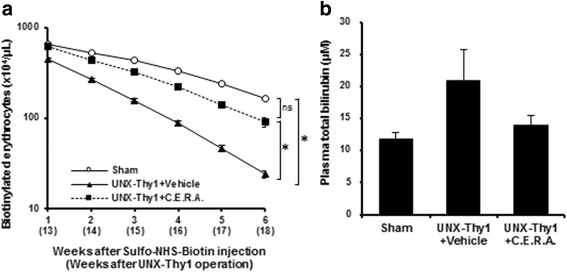
Results: Erythrocyte deformability progressively declined in CKD rats. Furthermore, erythrocyte turnover in the circulation drastically accelerated in CKD rats. With administration of C.E.R.A. at a dose sufficient to adequately control Hb, deterioration of erythrocyte deformability and turnover in CKD rats were significantly improved. Intracellular calcium, which plays a pivotal role in the mediation of erythrocyte quality, was significantly increased in CKD and was normalized by C.E.R.A.
Conclusion: C.E.R.A. treatment exerted a favorable effect not only on anemia but also on the improvement of erythrocyte quality. C.E.R.A. administered for the treatment of CKD-associated anemia may confer therapeutic benefits on erythrocytes.
Keywords: Anemia; Chronic kidney disease (CKD); Epoetin beta pegol (C.E.R.A.); Erythrocyte deformability; Erythrocyte turnover; Hematopoiesis; Intracellular calcium.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
This study is a non-clinical research. All animal procedures and experimental protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and conformed to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals published by Institution of Laboratory Animal Resources (ILAR).
Consent for publication
Not applicable (no individual person’s data).
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

