Apple endophytic microbiota of different rootstock/scion combinations suggests a genotype-specific influence
- PMID: 29374490
- PMCID: PMC5787276
- DOI: 10.1186/s40168-018-0403-x
Apple endophytic microbiota of different rootstock/scion combinations suggests a genotype-specific influence
Abstract
Background: High-throughput amplicon sequencing spanning conserved portions of microbial genomes (16s rRNA and ITS) was used in the present study to describe the endophytic microbiota associated with three apple varieties, "Royal Gala," "Golden Delicious," and "Honey Crisp," and two rootstocks, M.9 and M.M.111. The objectives were to (1) determine if the microbiota differs in different rootstocks and apple varieties and (2) determine if specific rootstock-scion combinations influence the microbiota composition of either component.
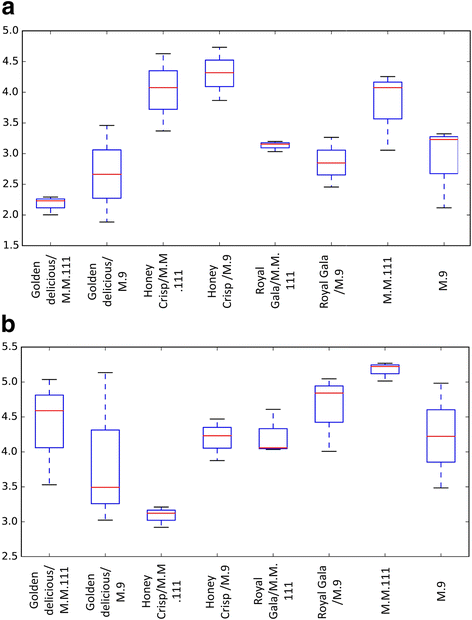
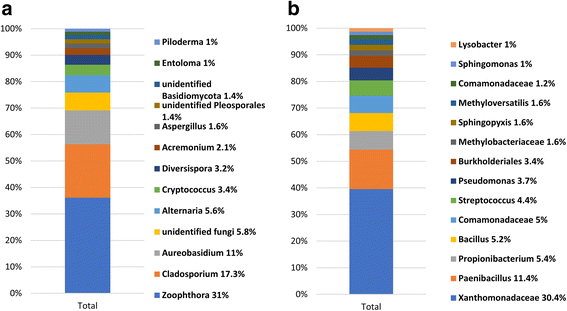
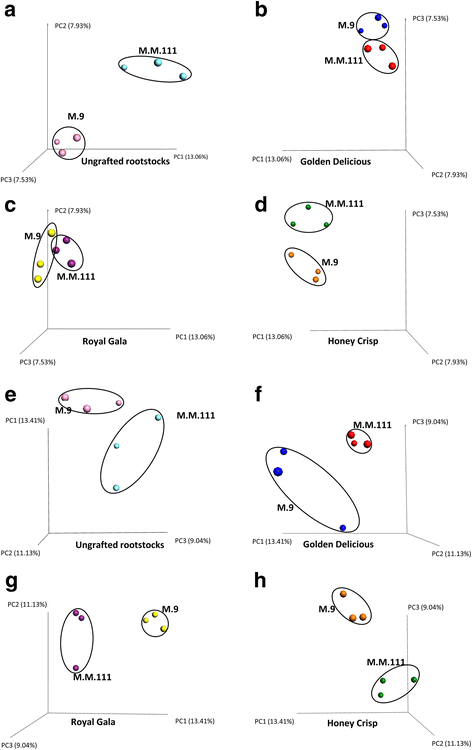
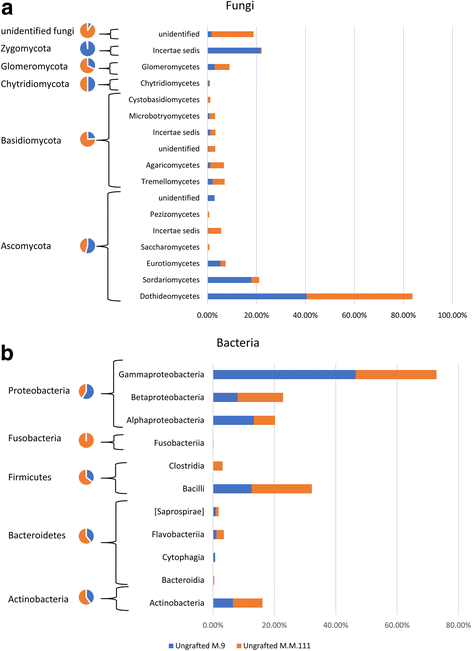
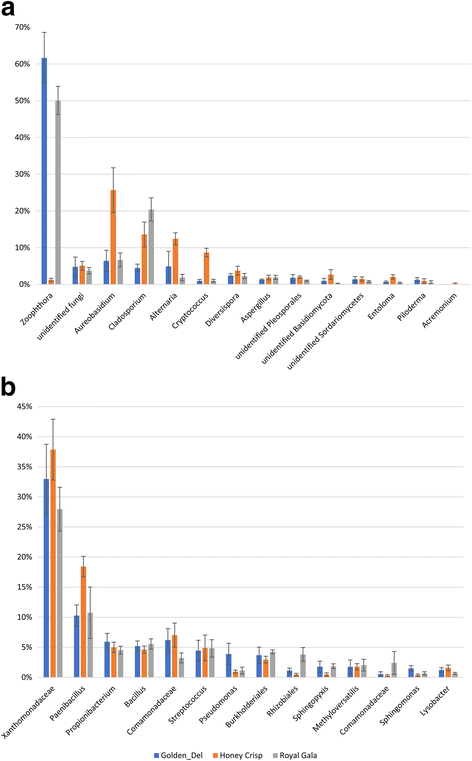
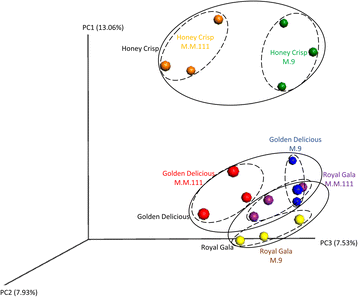
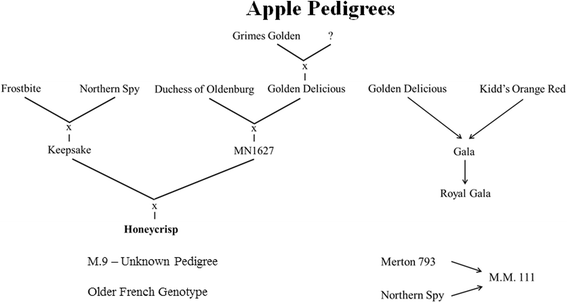
Results: Results indicated that Ascomycota (47.8%), Zygomycota (31.1%), and Basidiomycota (11.6%) were the dominant fungal phyla across all samples. The majority of bacterial sequences were assigned to Proteobacteria (58.4%), Firmicutes (23.8%), Actinobacteria (7.7%), Bacteroidetes (2%), and Fusobacteria (0.4%). Rootstocks appeared to influence the microbiota of associated grafted scion, but the effect was not statistically significant. Pedigree also had an impact on the composition of the endophytic microbiota, where closely-related cultivars had a microbial community that was more similar to each other than it was to a scion cultivar that was more distantly-related by pedigree. The more vigorous rootstock (M.M.111) was observed to possess a greater number of growth-promoting bacterial taxa, relative to the dwarfing rootstock (M.9).
Conclusions: The mechanism by which an apple genotype, either rootstock or scion, has a determinant effect on the composition of a microbial community is not known. The similarity of the microbiota in samples with a similar pedigree suggests the possibility of some level of co-evolution or selection as proposed by the "holobiont" concept in which metaorganisms have co-evolved. Clearly, however, the present information is only suggestive, and a more comprehensive analysis is needed.
Keywords: Apple; Endophytic microbiota; Holobiont; Rootstock; Scion cultivar.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Chagné D, Dayatilake D, Diack R, Oliver M, Ireland H, Watson A, Gardiner SE, Johnston JW, Schaffer RJ, Tustin S. Genetic and environmental control of fruit maturation, dry matter and firmness in apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.) Hortic Res. 2014;1:14046. doi: 10.1038/hortres.2014.46. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Costa F. MetaQTL analysis provides a compendium of genomic loci controlling fruit quality traits in apple. Tree Genet Genomes. 2015;11:819. doi: 10.1007/s11295-014-0819-9. - DOI
-
- Muranty H, Troggio M, Sadok IB, Rifaï MA, Auwerkerken A, Banchi E, Velasco R, Stevanato P, van de Weg WE, Di Guardo M, Kumar S, Laurens F, Bink MC. Accuracy and responses of genomic selection on key traits in apple breeding. Hortic Res. 2015;2:15060. doi: 10.1038/hortres.2015.60. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Duan N, Bai Y, Sun H, Wang N, Ma Y, Li M, Wang X, Jiao C, Legall N, Mao L, Wan S, Wang K, He T, Feng S, Zhang Z, Mao Z, Shen X, Chen X, Jiang Y, Wu S, Yin C, Ge S, Yang L, Jiang S, Xu H, Liu J, Wang D, Qu C, Wang Y, Zuo W, Xiang L, Liu C, Zhang D, Gao Y, Xu Y, Xu K, Chao T, Fazio G, Shu H, Zhong GY, Cheng L, Fei Z, Chen X. Genome re-sequencing reveals the history of apple and supports a two-stage model for fruit enlargement. Nat Commun. 2017;8:249. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00336-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

