Quality of life, sleep and rheumatoid arthritis (QUASAR): a protocol for a prospective UK mHealth study to investigate the relationship between sleep and quality of life in adults with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 29374666
- PMCID: PMC5829597
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-018752
Quality of life, sleep and rheumatoid arthritis (QUASAR): a protocol for a prospective UK mHealth study to investigate the relationship between sleep and quality of life in adults with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Introduction: People with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) frequently report reduced health-related quality of life (HRQoL), the impact one's health has on physical, emotional and social well-being. There are likely numerous causes for poor HRQoL, but people with RA have identified sleep disturbances as a key contributor to their well-being. This study will identify sleep/wake rhythm-associated parameters that predict HRQoL in patients with RA.
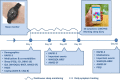
Methods and analysis: This prospective cohort study will recruit 350 people with RA, aged 18 years or older. Following completion of a paper-based baseline questionnaire, participants will record data on 10 symptoms including pain, fatigue and mood two times a day for 30 days using a study-specific mobile application (app). A triaxial accelerometer will continuously record daytime activity and estimate evening sleep parameters over the 30 days. Every 10 days following study initiation, participants will complete a questionnaire that measures disease specific (Arthritis Impact Measurement Scale 2-Short Form (AIMS2-SF)) and generic (WHOQOL-BREF) quality of life. A final questionnaire will be completed at 60 days after entering the study. The primary outcomes are the AIMS2-SF and WHOQOL-BREF. Structural equation modelling and latent trajectory models will be used to examine the relationship between sleep/wake rhythm-associated parameters and HRQoL, over time.
Ethics and dissemination: Results from this study will be disseminated at regional and international conferences, in peer-reviewed journals and Patient and Public Engagement events, as appropriate.
Keywords: epidemiology; rheumatology; sleep medicine.
© Article author(s) (or their employer(s) unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2018. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures




References
-
- NICE. Rheumatoid arthritis: national clinical guideline for management and treatment in adults. Clinical guideline [CG79]: National Institute of Health and Clinical Excellence, 2015.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
