Morphological analyses of the retinal photoreceptor cells in the nocturnally adapted owl monkeys
- PMID: 29375079
- PMCID: PMC5880819
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.17-0418
Morphological analyses of the retinal photoreceptor cells in the nocturnally adapted owl monkeys
Abstract
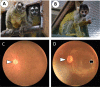
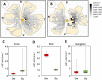
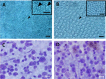
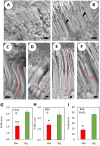
Owl monkeys are the only one species possessing the nocturnal lifestyles among the simian monkeys. Their eyes and retinas have been interested associating with the nocturnal adaptation. We examined the cellular specificity and electroretinogram (ERG) reactivity in the retina of the owl monkeys by comparison with the squirrel monkeys, taxonomically close-species and expressing diurnal behavior. Owl monkeys did not have clear structure of the foveal pit by the funduscope, whereas the retinal wholemount specimens indicated a small-condensed spot of the ganglion cells. There were abundant numbers of the rod photoreceptor cells in owl monkeys than those of the squirrel monkeys. However, the owl monkeys' retina did not possess superiority for rod cell-reactivity in the scotopic ERG responses. Scanning electron microscopic observation revealed that the rod cells in owl monkeys' retina had very small-sized inner and outer segments as compared with squirrel monkeys. Owl monkeys showed typical nocturnal traits such as rod-cell dominance. However, the individual photoreceptor cells seemed to be functionally weak for visual capacity, caused from the morphological immaturity at the inner and outer segments.
Keywords: evolution; owl monkey; photoreceptor cell; retina; squirrel monkey.
Figures
References
-
- Deldar A.1998. Blood and bone marrow. pp. 62–79. In: Textbook of Veterinary Histology, 5th ed. (Dellmann, H. D. and Eurell, J. A. eds). Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

