Intrinsic and Extrinsic Neuromodulation of Olfactory Processing
- PMID: 29375314
- PMCID: PMC5767172
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2017.00424
Intrinsic and Extrinsic Neuromodulation of Olfactory Processing
Abstract
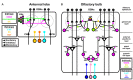
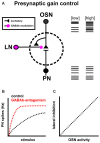
Neuromodulation is a ubiquitous feature of neural systems, allowing flexible, context specific control over network dynamics. Neuromodulation was first described in invertebrate motor systems and early work established a basic dichotomy for neuromodulation as having either an intrinsic origin (i.e., neurons that participate in network coding) or an extrinsic origin (i.e., neurons from independent networks). In this conceptual dichotomy, intrinsic sources of neuromodulation provide a "memory" by adjusting network dynamics based upon previous and ongoing activation of the network itself, while extrinsic neuromodulators provide the context of ongoing activity of other neural networks. Although this dichotomy has been thoroughly considered in motor systems, it has received far less attention in sensory systems. In this review, we discuss intrinsic and extrinsic modulation in the context of olfactory processing in invertebrate and vertebrate model systems. We begin by discussing presynaptic modulation of olfactory sensory neurons by local interneurons (LNs) as a mechanism for gain control based on ongoing network activation. We then discuss the cell-class specific effects of serotonergic centrifugal neurons on olfactory processing. Finally, we briefly discuss the integration of intrinsic and extrinsic neuromodulation (metamodulation) as an effective mechanism for exerting global control over olfactory network dynamics. The heterogeneous nature of neuromodulation is a recurring theme throughout this review as the effects of both intrinsic and extrinsic modulation are generally non-uniform.
Keywords: GABA; neuromodulation; olfaction; presynaptic gain control; sensory processing; serotonin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extrinsic neuromodulation in the rodent olfactory bulb.Cell Tissue Res. 2021 Jan;383(1):507-524. doi: 10.1007/s00441-020-03365-9. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Cell Tissue Res. 2021. PMID: 33355709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of Neural Microcircuits That Control Complex Dynamics in Olfactory Networks.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Jun 22;15:662184. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.662184. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34239417 Free PMC article.
-
Identified Serotonergic Modulatory Neurons Have Heterogeneous Synaptic Connectivity within the Olfactory System of Drosophila.J Neurosci. 2017 Aug 2;37(31):7318-7331. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0192-17.2017. Epub 2017 Jun 28. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28659283 Free PMC article.
-
Neuromodulation of Synaptic Transmission in the Main Olfactory Bulb.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018 Oct 8;15(10):2194. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15102194. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018. PMID: 30297631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-Type-Specific Modulation of Sensory Responses in Olfactory Bulb Circuits by Serotonergic Projections from the Raphe Nuclei.J Neurosci. 2016 Jun 22;36(25):6820-35. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3667-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27335411 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cortical feedback and gating in odor discrimination and generalization.PLoS Comput Biol. 2021 Oct 11;17(10):e1009479. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009479. eCollection 2021 Oct. PLoS Comput Biol. 2021. PMID: 34634035 Free PMC article.
-
Interhemispheric asymmetry of c-Fos expression in glomeruli and the olfactory tubercle following repeated odor stimulation.FEBS Open Bio. 2020 May;10(5):912-926. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12851. Epub 2020 Apr 13. FEBS Open Bio. 2020. PMID: 32237058 Free PMC article.
-
Muscarinic Modulation of Antennal Lobe GABAergic Local Neurons Shapes Odor Coding and Behavior.Cell Rep. 2019 Dec 3;29(10):3253-3265.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.10.125. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31801087 Free PMC article.
-
Kainate Receptors Play a Role in Modulating Synaptic Transmission in the Olfactory Bulb.Neuroscience. 2018 Nov 1;391:25-49. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.09.002. Epub 2018 Sep 11. Neuroscience. 2018. PMID: 30213766 Free PMC article.
-
Illuminating and Sniffing Out the Neuromodulatory Roles of Dopamine in the Retina and Olfactory Bulb.Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Aug 31;14:275. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.00275. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33110404 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Appel N. M., Mitchell W. M., Garlick R. K., Glennon R. A., Teitler M., De Souza E. B. (1990). Autoradiographic characterization of (+-)-1–(2,5-dimethoxy-4–[125I] iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane ([125I]DOI) binding to 5-HT2 and 5-HT1c receptors in rat brain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 255, 843–857. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

