Chronic Active Epstein-Barr Virus Disease
- PMID: 29375552
- PMCID: PMC5770746
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01867
Chronic Active Epstein-Barr Virus Disease
Abstract
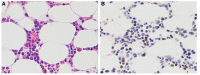
Chronic active Epstein-Barr virus (CAEBV) disease is a rare disorder in which persons are unable to control infection with the virus. The disease is progressive with markedly elevated levels of EBV DNA in the blood and infiltration of organs by EBV-positive lymphocytes. Patients often present with fever, lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, EBV hepatitis, or pancytopenia. Over time, these patients develop progressive immunodeficiency and if not treated, succumb to opportunistic infections, hemophagocytosis, multiorgan failure, or EBV-positive lymphomas. Patients with CAEBV in the United States most often present with disease involving B or T cells, while in Asia, the disease usually involves T or NK cells. The only proven effective treatment for the disease is hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Current studies to find a cause of this disease focus on immune defects and genetic abnormalities associated with the disease.
Keywords: DDX3X; Epstein–Barr virus lymphoma; chronic active Epstein–Barr virus; hemophagocytosis; infectious mononucleosis.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

