Platycodin D Inhibits Inflammatory Response in LPS-Stimulated Primary Rat Microglia Cells through Activating LXRα-ABCA1 Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 29375565
- PMCID: PMC5767310
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01929
Platycodin D Inhibits Inflammatory Response in LPS-Stimulated Primary Rat Microglia Cells through Activating LXRα-ABCA1 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
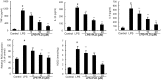
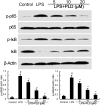
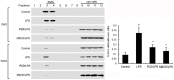
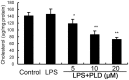
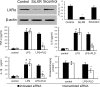
Platycodin D (PLD), an effective triterpenesaponin extracted from Platycodon grandiflorum, has been known to have anti-inflammatory effect. In the present study, we investigate the anti-inflammatory effects of PLD on LPS-induced inflammation in primary rat microglia cells. The results showed that PLD significantly inhibited LPS-induced ROS, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β production in primary rat microglia cells. PLD also inhibited LPS-induced NF-κB activation. Furthermore, our results showed that PLD prevented LPS-induced TLR4 translocation into lipid rafts via disrupting the formation of lipid rafts by inducing cholesterol efflux. In addition, PLD could activate LXRα-ABCA1 signaling pathway which induces cholesterol efflux from cells. The inhibition of inflammatory cytokines by PLD could be reversed by SiRNA of LXRα. In conclusion, these results indicated that PLD prevented LPS-induced inflammation by activating LXRα-ABCA1 signaling pathway, which disrupted lipid rafts and prevented TLR4 translocation into lipid rafts, thereby inhibiting LPS-induced inflammatory response.
Keywords: LPS; LXRα; NF-κB; TLR4; platycodin D.
Figures



References
-
- Prinz M, Kann O, Draheim HJ, Schumann RR, Kettenmann H, Weber JR, et al. Microglial activation by components of Gram-positive and -negative bacteria: distinct and common routes to the induction of ion channels and cytokines. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol (1999) 58:1078–89. 10.1097/00005072-199910000-00006 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

