Study on the diagnosis of small hepatocellular carcinoma caused by hepatitis B cirrhosis via multi-slice spiral CT and MRI
- PMID: 29375718
- PMCID: PMC5766070
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2017.7313
Study on the diagnosis of small hepatocellular carcinoma caused by hepatitis B cirrhosis via multi-slice spiral CT and MRI
Abstract
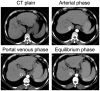
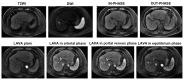
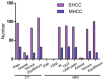
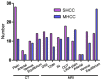
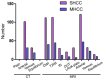
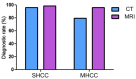
The present study compared the diagnostic accuracy of multi-slice spiral computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) on small hepatocellular carcinoma (SHCC) caused by hepatitis B cirrhosis. A total of 160 patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis were selected between January 2012 and April 2016, and 183 SHCC lesions were included in the present retrospective study. Patients were divided into the SHCC group (T stage) and the micro hepatocellular carcinoma (MHCC) group (T1 stage). There were a total of 129 SHCC lesions and 54 MHCC lesions identified. All patients underwent multiphasic CT and MRI imaging. The liver acquisition with volume acquisition (LAVA) technique was utilized for MRI. Furthermore, SPSS 20.0 was used for statistical analyses. LAVA in the arterial phase and CT in the arterial phase revealed significantly higher diagnostic rates for the diagnoses of 183 lesions. In addition, standard CT scan exhibited significantly reduced diagnostic rates in SHCC lesions. Results indicated that LAVA in the equilibrium phase had the lowest diagnostic rate in MHCC lesions, which was statistically significant (P<0.05). Overall, the diagnostic rate of CT (79.63%) for MHCC was significantly lower than that of MRI (96.29%) (P<0.05). However, the diagnostic rate of CT for SHCC (96.12%) was significantly higher than that for MHCC (79.63%) (P<0.05). MRI-LAVA in the arterial phase has the highest diagnostic rate for SHCC and MHCC. However, the diagnostic capability of MRI for MHCC lesions is superior to that of CT.
Keywords: diagnostic rate; magnetic resonance imaging; multi-slice spiral computed tomography; small hepatocellular carcinoma.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
