De novo assembly and characterization of the Hucho taimen transcriptome
- PMID: 29375797
- PMCID: PMC5773338
- DOI: 10.1002/ece3.3735
De novo assembly and characterization of the Hucho taimen transcriptome
Abstract
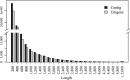
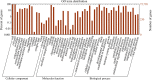
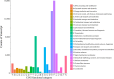
Taimen (Hucho taimen) is an important ecological and economic species that is classified as vulnerable by the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; however, limited genomic information is available on this species. RNA-Seq is a useful tool for obtaining genetic information and developing genetic markers for nonmodel species in addition to its application in gene expression profiling. In this study, we performed a comprehensive RNA-Seq analysis of taimen. We obtained 157 M clean reads (14.7 Gb) and used them to de novo assemble a high-quality transcriptome with a N50 size of 1,060 bp. In the assembly, 82% of the transcripts were annotated using several databases, and 14,666 of the transcripts contained a full open reading frame. The assembly covered 75% of the transcripts of Atlantic salmon and 57.3% of the protein-coding genes of rainbow trout. To learn about the genome evolution, we performed a systematic comparative analysis across 11 teleosts including eight salmonids and found 313 unique gene families in taimen. Using Atlantic salmon and rainbow trout transcriptomes as the background, we identified 250 positive selection transcripts. The pathway enrichment analysis revealed a unique characteristic of taimen: It possesses more immune-related genes than Atlantic salmon and rainbow trout; moreover, some genes have undergone strong positive selection. We also developed a pipeline for identifying microsatellite marker genotypes in samples and successfully identified 24 polymorphic microsatellite markers for taimen. These data and tools are useful for studying conservation genetics, phylogenetics, evolution among salmonids, and selective breeding for threatened taimen.
Keywords: Hucho taimen; RNA‐Seq; comparative transcript analysis; microsatellite markers; positive selection.
Figures




Similar articles
-
De novo transcriptome assembly, annotation and comparison of four ecological and evolutionary model salmonid fish species.BMC Genomics. 2018 Jan 8;19(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-4379-x. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29310597 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and antimicrobial activity of c-type lysozyme in taimen (Hucho taimen, Pallas).Dev Comp Immunol. 2016 Oct;63:156-62. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2016.06.003. Epub 2016 Jun 4. Dev Comp Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27267655
-
Gene expression profile of the taimen Hucho taimen in response to acute temperature changes.Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genomics Proteomics. 2021 Jun;38:100824. doi: 10.1016/j.cbd.2021.100824. Epub 2021 Mar 15. Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genomics Proteomics. 2021. PMID: 33743513
-
Genomic organization, expression and antimicrobial activity of a hepcidin from taimen (Hucho taimen, Pallas).Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016 Sep;56:303-309. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2016.07.027. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27452973
-
Characterizing and annotating the genome using RNA-seq data.Sci China Life Sci. 2017 Feb;60(2):116-125. doi: 10.1007/s11427-015-0349-4. Epub 2016 Jun 13. Sci China Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 27294835 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome analysis provides insights into copper toxicology in piebald naked carp (Gymnocypris eckloni).BMC Genomics. 2021 Jun 5;22(1):416. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07673-4. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34090338 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into Alexandrium minutum Nutrient Acquisition, Metabolism and Saxitoxin Biosynthesis through Comprehensive Transcriptome Survey.Biology (Basel). 2021 Aug 25;10(9):826. doi: 10.3390/biology10090826. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34571703 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of qPCR reference genes for taimen (Hucho taimen) under heat stress.Sci Rep. 2022 Jan 10;12(1):313. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-03872-x. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35013399 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andreji, J. , & Stráňai, I. (2013). Growth parameters of huchen Hucho hucho (L.) in the wild and under culture conditions. Archives of Polish Fisheries, 21(3), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.2478/aopf-2013-0015 - DOI
-
- Aubry, S. , Kelly, S. , Kümpers, B. M. , Smith‐Unna, R. D. , & Hibberd, J. M. (2014). Deep evolutionary comparison of gene expression identifies parallel recruitment of trans‐factors in two independent origins of C4 photosynthesis. PLoS Genetics, 10(6), e1004365 https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1004365 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balakirev, E. S. , Romanov, N. S. , Mikheev, P. B. , & Ayala, F. J. (2016). Complete mitochondrial genome of Siberian taimen, Hucho taimen not introgressed by the lenok subspecies, Brachymystax lenok and B. lenok tsinlingensis . Mitochondrial DNA. Part A, 27(2), 815–816. https://doi.org/10.3109/19401736.2014.919455 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Berthelot, C. , Brunet, F. , Chalopin, D. , Juanchich, A. , Bernard, M. , Noël, B. , … Guiguen, Y. (2014). The rainbow trout genome provides novel insights into evolution after whole‐genome duplication in vertebrates. Nature Communications, 5, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4657 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bolger, A. M. , Lohse, M. , & Usadel, B. (2014). Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics, 30(15), 2114–2120. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

