Comparison of Repeatability and Agreement between Swept-Source Optical Biometry and Dual-Scheimpflug Topography
- PMID: 29375908
- PMCID: PMC5742459
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/1516395
Comparison of Repeatability and Agreement between Swept-Source Optical Biometry and Dual-Scheimpflug Topography
Abstract
Purpose: To assess the repeatability and agreement of parameters obtained with two biometers and to compare the predictability.
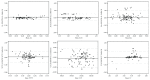
Methods: Biometry was performed on 101 eyes with cataract using the IOLMaster 700 and the Galilei G6. Three measurements were obtained per eye with each device, and repeatability was evaluated. The axial length (AL), anterior chamber depth (ACD), keratometry (K), white-to-white (WTW) corneal diameter, central corneal thickness (CCT), and lens thickness (LT) were measured and postoperative predictability was compared.
Results: Measurements could not be obtained with the IOLMaster 700 in one eye and in seven eyes with the Galilei G6 due to dense cataract. Both the IOLMaster 700 and Galilei G6 showed good repeatability, although the IOLMaster 700 showed better repeatability than the Galilei G6. There were no statistically significant differences in AL, ACD, steepest K, WTW, and LT (P > 0.050), although flattest K, mean K, and CCT differed (P < 0.050). The proportion of eyes with an absolute prediction error within 0.5 D was 85.0% for the IOLMaster 700 and was 80.0% for the Galilei G6 based on the SRK/T formula.
Conclusions: Two biometers showed high repeatability and relatively good agreements. The swept-source optical biometer demonstrated better repeatability, penetration, and an overall lower prediction error.
Figures
References
-
- Srivannaboon S., Chirapapaisan C., Chonpimai P., Loket S. Clinical comparison of a new swept-source optical coherence tomography–based optical biometer and a time-domain optical coherence tomography–based optical biometer. Journal of Cataract and Refractive Surgery. 2015;41(10):2224–2232. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2015.03.019. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Insight Photonic Solutions, Inc. Insight’s akinetic swept laser™ revolutionizing ophthalmic coherence tomography. May 2017, http://www.sweptlaser.com/3-generations-of-OCT.
-
- What’s next in laser and OCT? Swept-source OCT and nondamaging laser treatment. Review of Ophthalmology. 2013;20(Supplement)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

