Computational Intelligence-Assisted Understanding of Nature-Inspired Superhydrophobic Behavior
- PMID: 29375975
- PMCID: PMC5770681
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.201700520
Computational Intelligence-Assisted Understanding of Nature-Inspired Superhydrophobic Behavior
Abstract
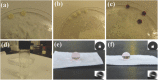
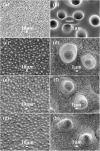
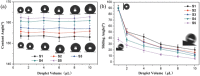
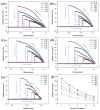
In recent years, state-of-the-art computational modeling of physical and chemical systems has shown itself to be an invaluable resource in the prediction of the properties and behavior of functional materials. However, construction of a useful computational model for novel systems in both academic and industrial contexts often requires a great depth of physicochemical theory and/or a wealth of empirical data, and a shortage in the availability of either frustrates the modeling process. In this work, computational intelligence is instead used, including artificial neural networks and evolutionary computation, to enhance our understanding of nature-inspired superhydrophobic behavior. The relationships between experimental parameters (water droplet volume, weight percentage of nanoparticles used in the synthesis of the polymer composite, and distance separating the superhydrophobic surface and the pendant water droplet in adhesive force measurements) and multiple objectives (water droplet contact angle, sliding angle, and adhesive force) are built and weighted. The obtained optimal parameters are consistent with the experimental observations. This new approach to materials modeling has great potential to be applied more generally to aid design, fabrication, and optimization for myriad functional materials.
Keywords: artificial neural networks; computational intelligence; evolutionary computation; superhydrophobic behavior.
Figures


References
-
- a) Rezayi T., Entezari M. H., Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 309, 795;
- b) Cho E.‐C., Chang‐Jian C.‐W., Chen H.‐C., Chuang K.‐S., Zheng J.‐H., Hsiao Y.‐S., Lee K.‐C., Huang J.‐H., Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 314, 347.
-
- a) Liu Y., Li X., Jin J., Liu J., Yan Y., Han Z., Ren L., Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 400, 498;
- b) Wang Y., Xue J., Wang Q., Chen Q., Ding J., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 3370. - PubMed
-
- a) Xue Z., Wang S., Lin L., Chen L., Liu M., Feng L., Jiang L., Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4270; - PubMed
- b) Lu Y., Sathasivam S., Song J., Chen F., Xu W., Carmalt C. J., Parkin I. P., J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 11628.
-
- a) Lu Y., Sathasivam S., Song J., Crick C. R., Carmalt C. J., Parkin I. P., Science 2015, 347, 1132; - PubMed
- b) Sutha S., Suresh S., Raj B., Ravi K. R., Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2017, 165, 128;
- c) Wang P., Chen M., Han H., Fan X., Liu Q., Wang J., J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 7869.
-
- a) Barthlott W., Neinhuis C., Planta 1997, 202, 1;
- b) Parkin I. P., Palgrave R. G., J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 1689.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
