Virtual assessment of stereoscopic viewing of digital breast tomosynthesis projection images
- PMID: 29376103
- PMCID: PMC5771135
- DOI: 10.1117/1.JMI.5.1.015501
Virtual assessment of stereoscopic viewing of digital breast tomosynthesis projection images
Abstract
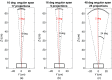
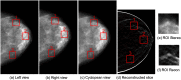
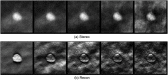
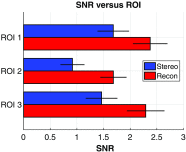
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) acquires a series of projection images from different angles as an x-ray source rotates around the breast. Such imaging geometry lends DBT naturally to stereoscopic viewing as two projection images with a reasonable separation angle can easily form a stereo pair. This simulation study assessed the efficacy of stereo viewing of DBT projection images. Three-dimensional computational breast phantoms with realistically shaped synthetic lesions were scanned by three simulated DBT systems. The projection images were combined into a sequence of stereo pairs and presented to a stereomatching-based model observer for deciding lesion presence. Signal-to-noise ratio was estimated, and the detection performance with stack viewing of reconstructed slices was the benchmark. We have shown that: (1) stereo viewing of projection images may underperform stack viewing of reconstructed slices for current DBT geometries; (2) DBT geometries may impact the efficacy of the two viewing modes differently: narrow-arc and wide-arc geometries may be better for stereo viewing and stack viewing, respectively; (3) the efficacy of stereo viewing may be more robust than stack viewing to reductions in dose. While in principle stereo viewing is potentially effective for visualizing DBT data, effective stereo viewing may require specifically optimized DBT image acquisition.
Keywords: digital breast tomosynthesis; disparity; model observer; reconstruction; stereo matching; stereoscopic viewing.
Figures

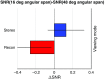
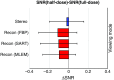
Similar articles
-
Computational assessment of stereoscopic viewing a sequence of stereo pairs of breast tomosynthesis projection images.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2014;2014:6048-51. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2014.6945008. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2014. PMID: 25571376
-
Lesion detection in digital breast tomosynthesis: human reader experiments indicate no benefit from the integration of information from multiple planes.J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2023 Feb;10(Suppl 1):S11915. doi: 10.1117/1.JMI.10.S1.S11915. Epub 2023 Jun 26. J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2023. PMID: 37378263 Free PMC article.
-
Digital breast tomosynthesis: observer performance of clustered microcalcification detection on breast phantom images acquired with an experimental system using variable scan angles, angular increments, and number of projection views.Radiology. 2014 Dec;273(3):675-85. doi: 10.1148/radiol.14132722. Epub 2014 Jul 7. Radiology. 2014. PMID: 25007048 Free PMC article.
-
Breast tomosynthesis: What do we know and where do we stand?Diagn Interv Imaging. 2019 Oct;100(10):537-551. doi: 10.1016/j.diii.2019.07.012. Epub 2019 Aug 16. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2019. PMID: 31427217 Review.
-
Digital breast tomosynthesis: Image acquisition principles and artifacts.Clin Imaging. 2019 May-Jun;55:188-195. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2018.07.013. Epub 2018 Sep 13. Clin Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30236642 Review.
References
-
- Smith A., “Fundamentals of breast tomosynthesis,” in Hologic Breast Imaging White Papers, Hologic Inc., Bedford, Mass: (2008).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

