Oil for the cancer engine: The cross-talk between oncogenic signaling and polyamine metabolism
- PMID: 29376126
- PMCID: PMC5783676
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aar2606
Oil for the cancer engine: The cross-talk between oncogenic signaling and polyamine metabolism
Abstract
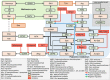
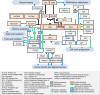
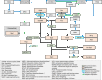
The study of metabolism has provided remarkable information about the biological basis and therapeutic weaknesses of cancer cells. Classic biochemistry established the importance of metabolic alterations in tumor biology and revealed the importance of various metabolite families to the tumorigenic process. We have evidence of the central role of polyamines, small polycatonic metabolites, in cell proliferation and cancer growth from these studies. However, how cancer cells activate this metabolic pathway and the molecular cues behind the oncogenic action of polyamines has remained largely obscure. In contrast to the view of metabolites as fuel (anabolic intermediates) for cancer cells, polyamines are better defined as the oil that lubricates the cancer engine because they affect the activity of biological processes. Modern research has brought back to the limelight this metabolic pathway, providing a strong link between genetic, metabolic, and signaling events in cancer. In this review, we enumerate and discuss current views of the regulation and activity of polyamine metabolism in tumor cell biology.
Figures
References
-
- Hanahan D., Weinberg R. A., Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 144, 646–674 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Koppenol W. H., Bounds P. L., Dang C. V., Otto Warburg’s contributions to current concepts of cancer metabolism. Nat. Rev. Cancer 11, 325–337 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Lunt S. Y., Vander Heiden M. G., Aerobic glycolysis: Meeting the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 27, 441–464 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Chiang P. K., Gordon R. K., Tal J., Zeng G. C., Doctor B. P., Pardhasaradhi K., McCann P. P., S-Adenosylmethionine and methylation. FASEB J. 10, 471–480 (1996). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources